Encephalitis: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
What are the symptoms of encephalitis?
Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain, usually caused by a viral infection. The symptoms of encephalitis can vary depending on the severity of the inflammation and the part of the brain affected. Common symptoms include:
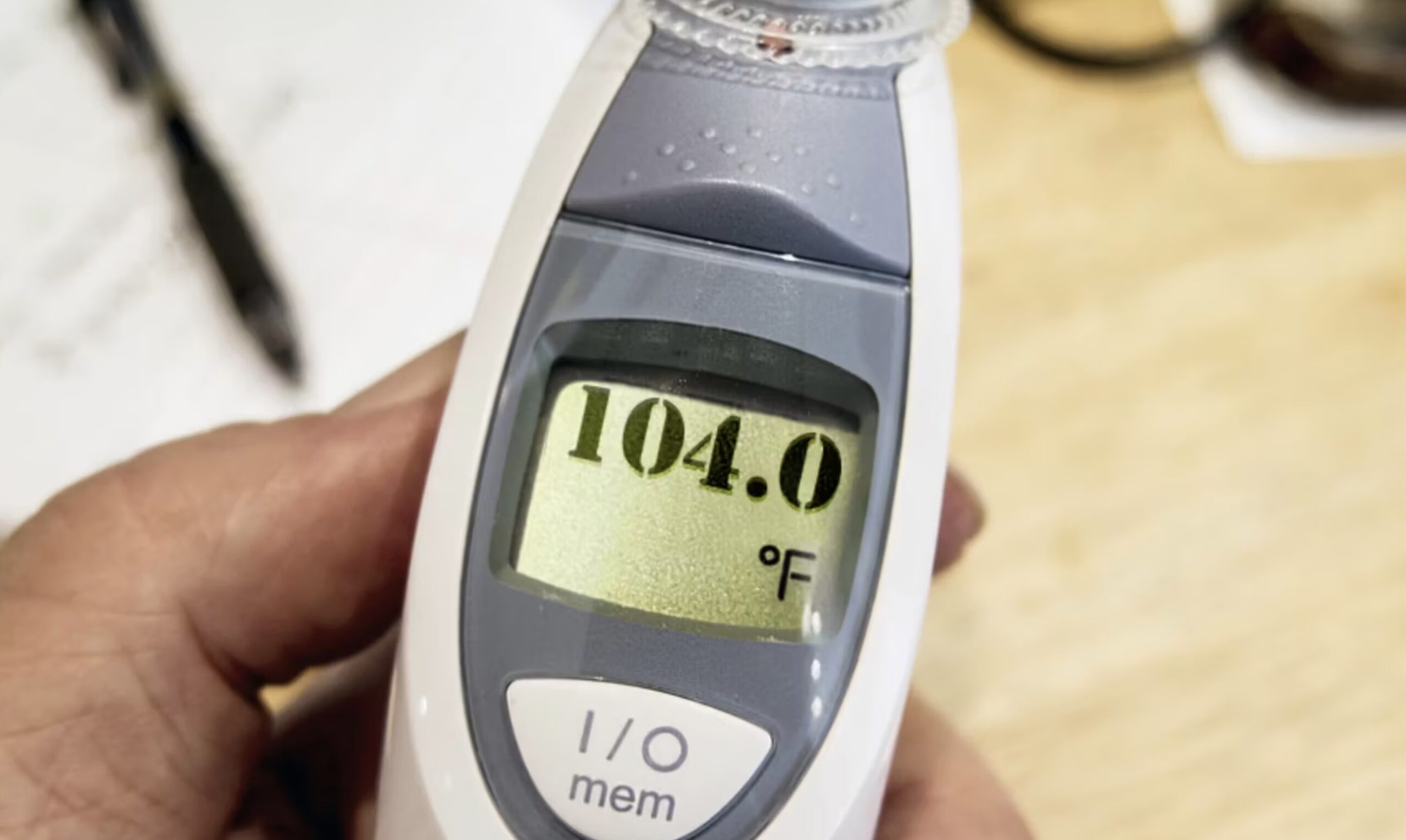
- Fever: A high fever is often the first sign of encephalitis.
- Headache: Severe headaches are common in people with encephalitis.
- Confusion: Encephalitis can cause confusion, disorientation, and difficulty concentrating.
- Seizures: Seizures may occur in some cases of encephalitis.
- Changes in Personality or Behavior: Encephalitis can cause changes in personality, behavior, or mood.
- Hallucinations: Some people with encephalitis may experience hallucinations, seeing or hearing things that are not real.
- Difficulty Speaking or Understanding Speech: Encephalitis can affect the areas of the brain responsible for language, leading to difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
- Weakness or Paralysis: Encephalitis can cause weakness or paralysis in parts of the body.
- Loss of Consciousness: In severe cases, encephalitis can cause loss of consciousness or coma.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some people with encephalitis may experience nausea and vomiting.
- Stiff Neck: In some cases, encephalitis can cause a stiff neck, especially if the inflammation spreads to the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord (meninges).
- Sensitivity to Light: Encephalitis can cause sensitivity to light (photophobia).
It’s important to note that not everyone with encephalitis will experience all of these symptoms, and symptoms can vary widely from person to person. In some cases, especially in mild cases of encephalitis, symptoms may be mild or flu-like and may go unnoticed or be attributed to other causes. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of encephalitis, especially fever, headache, and confusion, it’s important to seek medical attention from your healthcare provider promptly for diagnosis and treatment.
What are the causes of encephalitis?
Encephalitis is most commonly caused by viral infections, but it can also be caused by bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders, and other factors. Some of the most common causes of encephalitis include:
- Viral Infections:
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): HSV is the most common cause of viral encephalitis in the United States. It can be transmitted through close contact with an infected person.
- Enteroviruses: These viruses are common and usually cause mild symptoms, but they can sometimes lead to encephalitis.
- Arboviruses: These are viruses transmitted by mosquitoes and ticks, such as West Nile virus, Eastern equine encephalitis virus, and Japanese encephalitis virus.
- Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV): VZV is the virus that causes chickenpox and shingles. It can rarely cause encephalitis, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
- Bacterial Infections:
- Bacterial infections that can cause encephalitis include Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Lyme disease (caused by Borrelia burgdorferi), and tuberculosis (TB).
- Autoimmune Disorders:
- Autoimmune encephalitis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy brain cells, leading to inflammation. This can be triggered by infections, tumors, or other factors.
- Other Causes:
- Fungal Infections: Fungal infections such as cryptococcosis and histoplasmosis can rarely cause encephalitis.
- Parasitic Infections: Parasitic infections such as toxoplasmosis can also cause encephalitis, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
- Non-infectious Causes: Encephalitis can also be caused by non-infectious factors, such as reactions to certain medications, chemicals, or autoimmune disorders.
It’s important to note that encephalitis can be a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. Treatment may include antiviral or antibacterial medications, corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and supportive care to manage symptoms. The specific treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the encephalitis.
What is the treatment for encephalitis?
The treatment for encephalitis depends on the underlying cause of the condition and the severity of symptoms. In many cases, hospitalization is necessary, especially for severe cases of encephalitis. Treatment may include:
- Antiviral Medications: If the encephalitis is caused by a viral infection, antiviral medications may be prescribed. Common antiviral medications used to treat encephalitis include acyclovir for herpes simplex virus (HSV) and ganciclovir for cytomegalovirus (CMV).
- Antibiotics: If the encephalitis is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed. The choice of antibiotic will depend on the specific bacteria causing the infection.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, may be used to reduce inflammation in the brain and help control symptoms.
- Anticonvulsant Medications: If seizures occur, anticonvulsant medications may be prescribed to help control them.
- Supportive Care: Supportive care may be provided to manage symptoms and help the patient recover. This may include intravenous fluids, pain relief medications, and respiratory support if needed.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy may be recommended to help improve strength, coordination, and mobility in patients recovering from encephalitis.
- Monitoring: Patients with encephalitis may require close monitoring, especially if they are experiencing severe symptoms. Monitoring may include regular neurological assessments and imaging studies to evaluate the brain.
- Treatment of Complications: If complications such as brain swelling or increased intracranial pressure occur, additional treatments may be necessary.
It’s important for patients with encephalitis to receive prompt and appropriate treatment to reduce the risk of complications and improve outcomes. The specific treatment approach will depend on the underlying cause of the encephalitis and the individual patient’s condition.