Blepharitis: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of blepharitis?
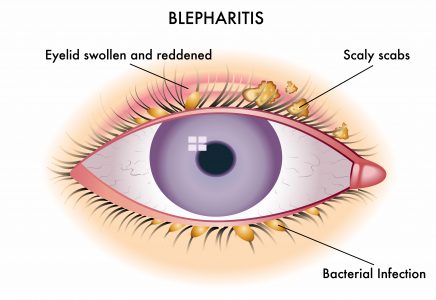
Blepharitis is a common and chronic condition characterized by inflammation of the eyelids, specifically at the base of the eyelashes. Symptoms of blepharitis can vary but may include:
- Redness: The edges of the eyelids may appear red and swollen.
- Itchiness: The eyelids may feel itchy or irritated.
- Burning sensation: Some people with blepharitis may experience a burning sensation in the eyes.
- Crusting: The eyelids may develop crusts or scales, particularly upon waking in the morning.
- Tearing: Excessive tearing or watery eyes may occur.
- Sensitivity to light: Some people with blepharitis may be sensitive to light (photophobia).
- Grittiness or foreign body sensation: The eyes may feel gritty, as if there is a foreign body present.
- Dry eyes: Blepharitis can disrupt the normal production of tears, leading to dry eye symptoms.
- Eyelash problems: The eyelashes may become misdirected or fall out.
- Blurry vision: In some cases, blepharitis can cause blurry vision, especially if it affects the function of the tear glands.
The symptoms of blepharitis can come and go and may vary in severity. They can also be similar to those of other eye conditions, so it’s important to see an eye care professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Treatment for blepharitis typically involves a combination of eyelid hygiene, warm compresses, and medications to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
What are the causes of blepharitis?
Blepharitis can have several causes, and it is often a chronic condition that requires ongoing management. Some common causes and contributing factors of blepharitis include:
- Bacterial infection: Bacterial overgrowth, particularly of Staphylococcus species, on the eyelids can lead to blepharitis. The bacteria produce toxins that can cause inflammation of the eyelid margins.
- Meibomian gland dysfunction: Dysfunction of the meibomian glands, which are responsible for producing the oily layer of the tear film, can contribute to blepharitis. Blocked or inflamed meibomian glands can lead to an unstable tear film and dry eye symptoms.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: Blepharitis is commonly associated with seborrheic dermatitis, a skin condition characterized by red, flaky, and oily skin. Seborrheic dermatitis can affect the scalp, face, and eyelids.
- Allergic reactions: Allergies to substances such as makeup, eye drops, or contact lens solutions can contribute to blepharitis symptoms.
- Demodex mites: These microscopic mites are commonly found on the skin, including the eyelids. An overgrowth of Demodex mites can contribute to inflammation of the eyelids.
- Dry eye syndrome: Chronic dry eye can lead to inflammation of the eyelids and contribute to blepharitis symptoms.
- Poor eyelid hygiene: Not cleaning the eyelids properly can lead to a buildup of debris, oils, and bacteria, contributing to blepharitis.
- Contact lens use: Improper use or hygiene practices with contact lenses can increase the risk of blepharitis.
- Systemic conditions: Certain systemic conditions, such as rosacea, can increase the risk of developing blepharitis.
It’s important to determine the underlying cause of blepharitis to develop an effective treatment plan. Treatment typically involves a combination of eyelid hygiene practices, warm compresses, and medications to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
What is the treatment for blepharitis?
The treatment for blepharitis typically involves a combination of eyelid hygiene practices, warm compresses, and medications to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms. The specific treatment approach may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some common treatments for blepharitis:
- Eyelid hygiene: Regular eyelid hygiene is essential for managing blepharitis. This includes gently cleaning the eyelids and lashes with a warm washcloth or eyelid scrub solution to remove debris and oils. Your healthcare provider may recommend specific eyelid hygiene products.
- Warm compresses: Applying warm compresses to the eyelids can help soften the oils in the meibomian glands and improve their function. This can help reduce symptoms and prevent blockages in the glands.
- Medicated eye drops or ointments: Your healthcare provider may prescribe medicated eye drops or ointments to reduce inflammation and treat bacterial or fungal infections, if present. These medications may contain antibiotics, corticosteroids, or other anti-inflammatory agents.
- Oral medications: In some cases, oral medications such as antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to help manage blepharitis symptoms.
- Lid scrubs: Your healthcare provider may recommend using lid scrubs or eyelid wipes to help clean the eyelids and lashes and reduce inflammation.
- Nutritional supplements: Omega-3 fatty acid supplements may help improve the function of the meibomian glands and reduce inflammation in some cases of blepharitis.
- Management of underlying conditions: If blepharitis is associated with underlying conditions such as rosacea or seborrheic dermatitis, treatment of these conditions may help improve blepharitis symptoms.
- Avoiding irritants: Avoiding eye makeup, contact lenses, or other products that can irritate the eyes or contribute to blepharitis may help improve symptoms.
It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for treatment and to attend follow-up appointments as needed to monitor your condition. Chronic blepharitis may require long-term management to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.