Geographic Tongue: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of geographic tongue?
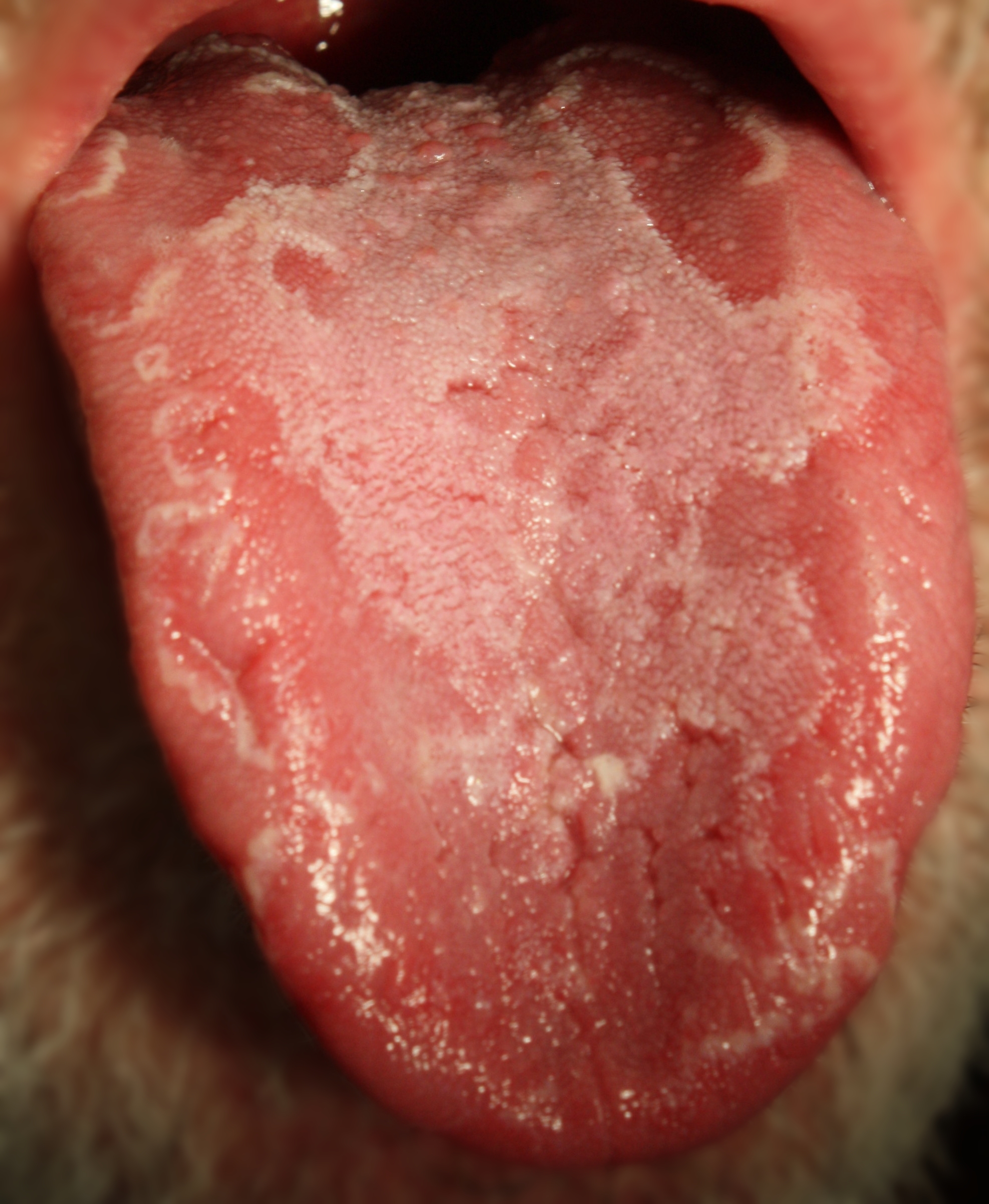
Geographic tongue, also known as benign migratory glossitis, is a harmless condition that affects the tongue, causing patches on the surface to become inflamed and change in appearance. The main symptom of geographic tongue is the presence of irregular, smooth, red patches on the surface of the tongue that may change in shape and size over time. These patches may resemble a map, giving the condition its name.
Other common symptoms of geographic tongue include:
- Pain or discomfort: Some people with geographic tongue may experience mild pain or discomfort, especially when eating spicy, acidic, or hot foods.
- Sensitivity to certain foods: Foods that irritate the tongue, such as spicy or acidic foods, may cause discomfort or a burning sensation.
- Swollen or tender tongue: The patches on the tongue may become swollen or tender, especially during flare-ups.
- Appearance changes: The appearance of the patches on the tongue may change frequently, with the patches appearing and disappearing in different areas of the tongue.
- White patches: In some cases, white patches or lines may appear on the surface of the tongue, especially where the patches have disappeared.
- Burning sensation: Some people with geographic tongue may experience a burning sensation on the tongue, especially when eating certain foods.
It’s important to note that geographic tongue is usually a benign condition that does not require treatment unless it is causing symptoms such as pain or discomfort. If you are experiencing symptoms of geographic tongue, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider or dentist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
What are the causes of geographic tongue?
The exact cause of geographic tongue is not known, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Some factors that may contribute to the development of geographic tongue include:
- Genetics: Geographic tongue tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition to the condition.
- Immune system response: Some researchers believe that geographic tongue may be an immune system response, as the condition is more common in people with certain autoimmune diseases, such as psoriasis.
- Hormonal factors: Changes in hormone levels, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopause, may play a role in the development of geographic tongue.
- Stress: Stress and anxiety have been associated with an increased risk of geographic tongue in some individuals.
- Environmental factors: Certain environmental factors, such as tobacco use, spicy or acidic foods, and poor oral hygiene, may exacerbate the condition.
It’s important to note that geographic tongue is usually a benign condition that does not require treatment unless it is causing symptoms such as pain or discomfort. If you are experiencing symptoms of geographic tongue, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider or dentist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
What is the treatment for geographic tongue?
Treatment for geographic tongue is usually not necessary, as the condition is typically harmless and does not cause any symptoms in most cases. However, if you are experiencing discomfort or other symptoms associated with geographic tongue, your healthcare provider may recommend the following:
- Oral hygiene: Good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing your teeth and tongue regularly and using a tongue scraper, can help reduce irritation and keep the tongue clean.
- Avoiding irritants: Avoiding foods and beverages that may irritate the tongue, such as spicy, acidic, or hot foods, can help reduce discomfort.
- Mouthwash: Using an antiseptic mouthwash can help reduce the risk of infection and keep the mouth clean.
- Topical treatments: In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend applying a topical corticosteroid or antifungal medication to reduce inflammation or treat any underlying infections.
- Dietary changes: Some healthcare providers may recommend dietary changes, such as avoiding foods that may trigger flare-ups, to help manage symptoms.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider or dentist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management if you have any concerns about your tongue or oral health.