High Cholesterol: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of high cholesterol?
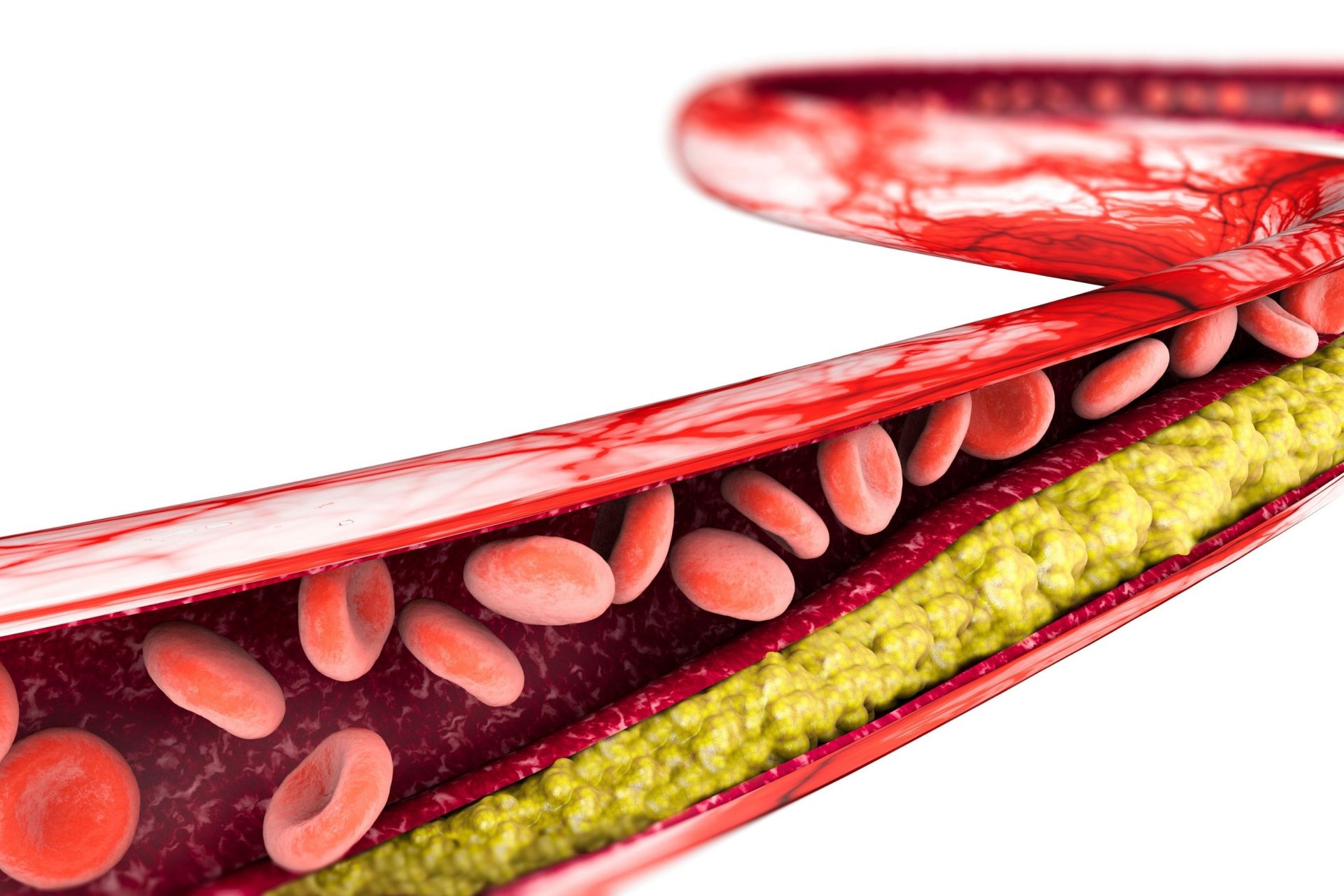
High cholesterol typically doesn’t cause any symptoms, so it’s often referred to as a “silent” condition. The only way to know if you have high cholesterol is through a blood test. However, extremely high cholesterol levels may cause deposits of cholesterol to form in the skin or tendons, leading to visible signs such as:
- Yellowish patches or bumps on the skin, commonly around the eyes (xanthelasma).
- Yellowish, raised areas of skin on the elbows, knees, hands, or feet (xanthomas).
- White or yellowish ring around the cornea of the eye (arcus senilis), particularly in older adults.
It’s important to get your cholesterol levels checked regularly, as high cholesterol can increase your risk of heart disease and stroke. It is important to see a healthcare provider to have you cholesterol levels checked.
What are the causes of high cholesterol?
High cholesterol can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Diet: Consuming foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can raise your cholesterol levels.
- Weight: Being overweight or obese can increase your LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and decrease your HDL (“good”) cholesterol.
- Physical activity: Lack of regular physical activity can lead to higher LDL cholesterol and lower HDL cholesterol levels.
- Age and gender: Cholesterol levels tend to increase with age, and men are more likely to have higher cholesterol levels than premenopausal women.
- Genetics: Your genes can influence how your body processes cholesterol. Some people have a genetic predisposition to high cholesterol.
- Other health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, kidney disease, and liver disease, can affect cholesterol levels.
- Smoking: Smoking can lower HDL cholesterol and damage the walls of your blood vessels, making them more susceptible to cholesterol buildup. So consider quitting smoking.
- Medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids, diuretics, and some HIV medications, can increase cholesterol levels.
It’s important to address any underlying causes of high cholesterol to reduce your risk of heart disease and stroke. This may involve lifestyle changes, such as improving your diet and increasing physical activity, as well as medication in some cases. Consult your healthcare provider.
What is the treatment for high cholesterol?
The treatment for high cholesterol typically involves lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Here are some common approaches:
- Lifestyle changes:
- Healthy diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol.
- Weight management: Maintain a healthy weight or lose weight if you’re overweight.
- Physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week, along with muscle-strengthening exercises on two or more days a week.
- Quit smoking: Smoking damages your blood vessels and can raise your cholesterol levels.
- Medications:
- Statins: These are the most commonly prescribed medications for high cholesterol. They work by blocking a substance your liver needs to make cholesterol.
- Ezetimibe (Zetia): This medication helps reduce the amount of cholesterol your body absorbs from your diet.
- PCSK9 inhibitors: These medications help lower LDL cholesterol levels by increasing the liver’s ability to remove LDL cholesterol from the blood.
- Bile acid-binding resins: These medications help remove cholesterol from your body, but they can cause digestive side effects.
- Combination therapy: In some cases, your doctor may prescribe a combination of medications to help lower your cholesterol levels more effectively.
- Regular monitoring: Your doctor will likely recommend regular blood tests to monitor your cholesterol levels and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.