Reconstructive Surgery
What are common types of reconstructive surgery?
Reconstructive surgery is a type of surgery performed to correct physical deformities, restore function, or improve appearance following injury, disease, or birth defects. There are several common types of reconstructive surgery, including:
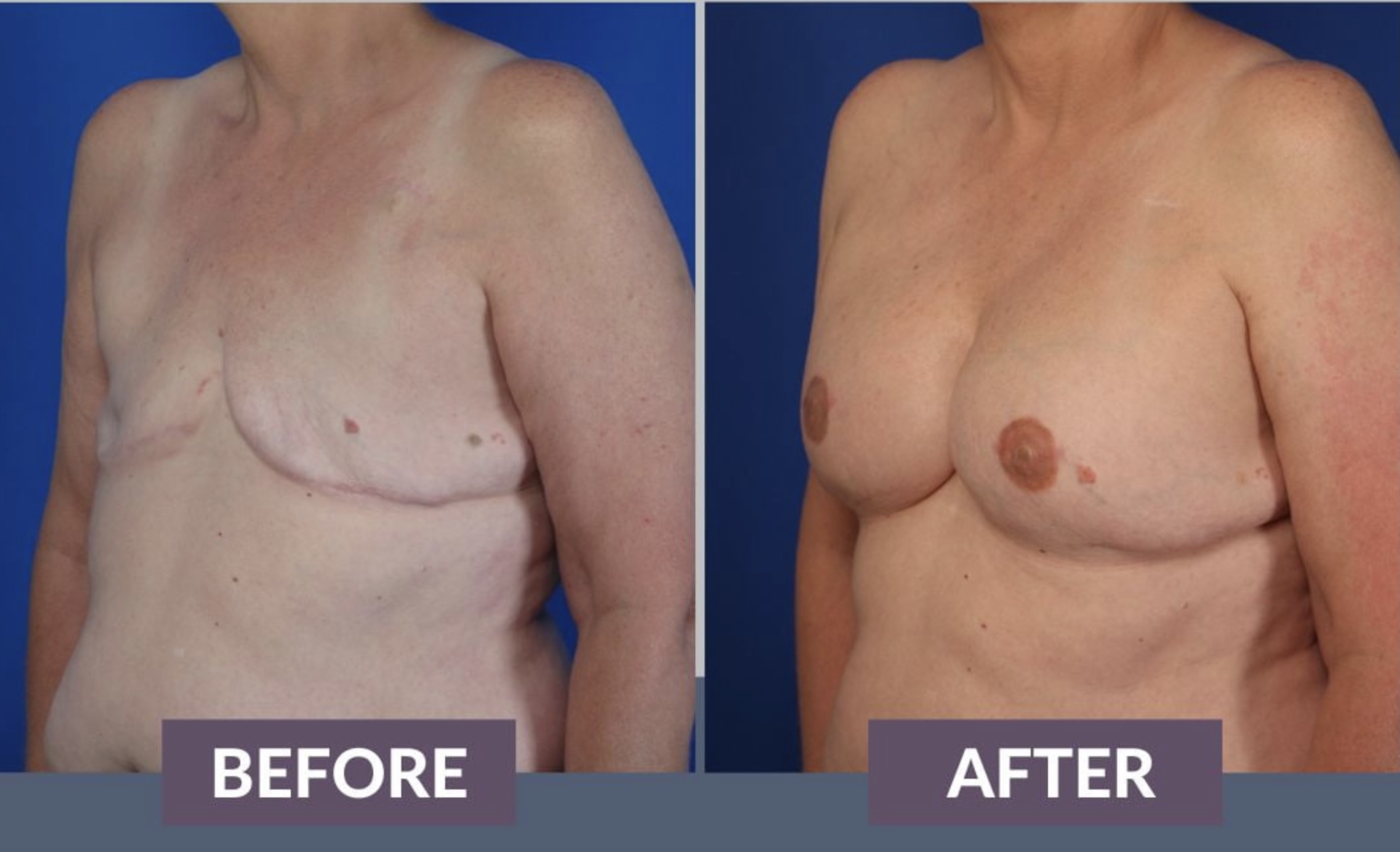
- Breast Reconstruction: Breast reconstruction is often performed after a mastectomy (removal of the breast) due to breast cancer. It can involve using implants or tissue from other parts of the body to recreate a natural-looking breast.
- Skin Grafts: Skin grafts are used to repair skin that has been damaged or lost due to injury, burns, or surgery. A skin graft involves taking a thin layer of skin from one area of the body (the donor site) and transplanting it to the damaged area.
- Flap Surgery: Flap surgery involves moving tissue, along with its blood supply, from one part of the body to another to reconstruct or repair a damaged area. Flaps can be used for reconstructive purposes in various areas of the body, including the face, breast, and limbs.
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair: Cleft lip and palate are birth defects that affect the upper lip and roof of the mouth. Reconstructive surgery can help repair these defects to improve speech, eating, and appearance.
- Hand Surgery: Hand surgery can be performed to repair injuries, correct deformities, or improve function in the hands. This may include tendon repair, nerve repair, or joint reconstruction.
- Facial Reconstruction: Facial reconstruction surgery can be performed to repair facial injuries, correct facial deformities, or improve facial appearance. This may include procedures such as rhinoplasty (nose surgery), otoplasty (ear surgery), or facial bone reconstruction.
- Microsurgery: Microsurgery involves using a microscope and tiny instruments to perform intricate surgical procedures, such as replanting severed limbs or repairing small blood vessels.
- Scar Revision: Scar revision surgery is performed to improve the appearance of scars, making them less noticeable or more cosmetically pleasing.
These are just a few examples of the many types of reconstructive surgery that are available. The specific type of reconstructive surgery recommended will depend on the individual’s condition and treatment goals.
Will insurance cover reconstructive surgery?
Whether insurance will cover reconstructive surgery depends on several factors, including the reason for the surgery, the type of insurance coverage you have, and the specific terms of your insurance policy. In general, insurance is more likely to cover reconstructive surgery than cosmetic surgery, as reconstructive surgery is often considered medically necessary to correct a physical deformity, restore function, or improve health.
Some common situations where insurance may cover reconstructive surgery include:
- Post-Mastectomy Breast Reconstruction: Federal law requires insurance plans that cover mastectomies to also cover reconstructive surgery, including surgery on the other breast to achieve symmetry.
- Reconstruction After Trauma or Injury: Insurance may cover reconstructive surgery to repair physical deformities or restore function following trauma, burns, or accidents.
- Reconstruction After Cancer Surgery: Insurance may cover reconstructive surgery following surgery to remove cancerous tumors, such as breast reconstruction after a mastectomy or facial reconstruction after surgery for head and neck cancer.
- Corrective Surgery for Birth Defects: Insurance may cover surgery to correct birth defects, such as cleft lip and palate or hand deformities.
- Reconstruction After Weight Loss Surgery: Insurance may cover reconstructive surgery, such as abdominoplasty or body lift surgery, following significant weight loss to remove excess skin and improve body contour.
It’s important to check with your insurance provider to understand what is covered under your plan. You may need to obtain pre-authorization for the surgery and meet certain criteria to qualify for coverage. Your healthcare provider can also help you navigate the insurance approval process and provide documentation to support the medical necessity of the surgery.