Gynecomastia: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
What are the symptoms of gynecomastia?
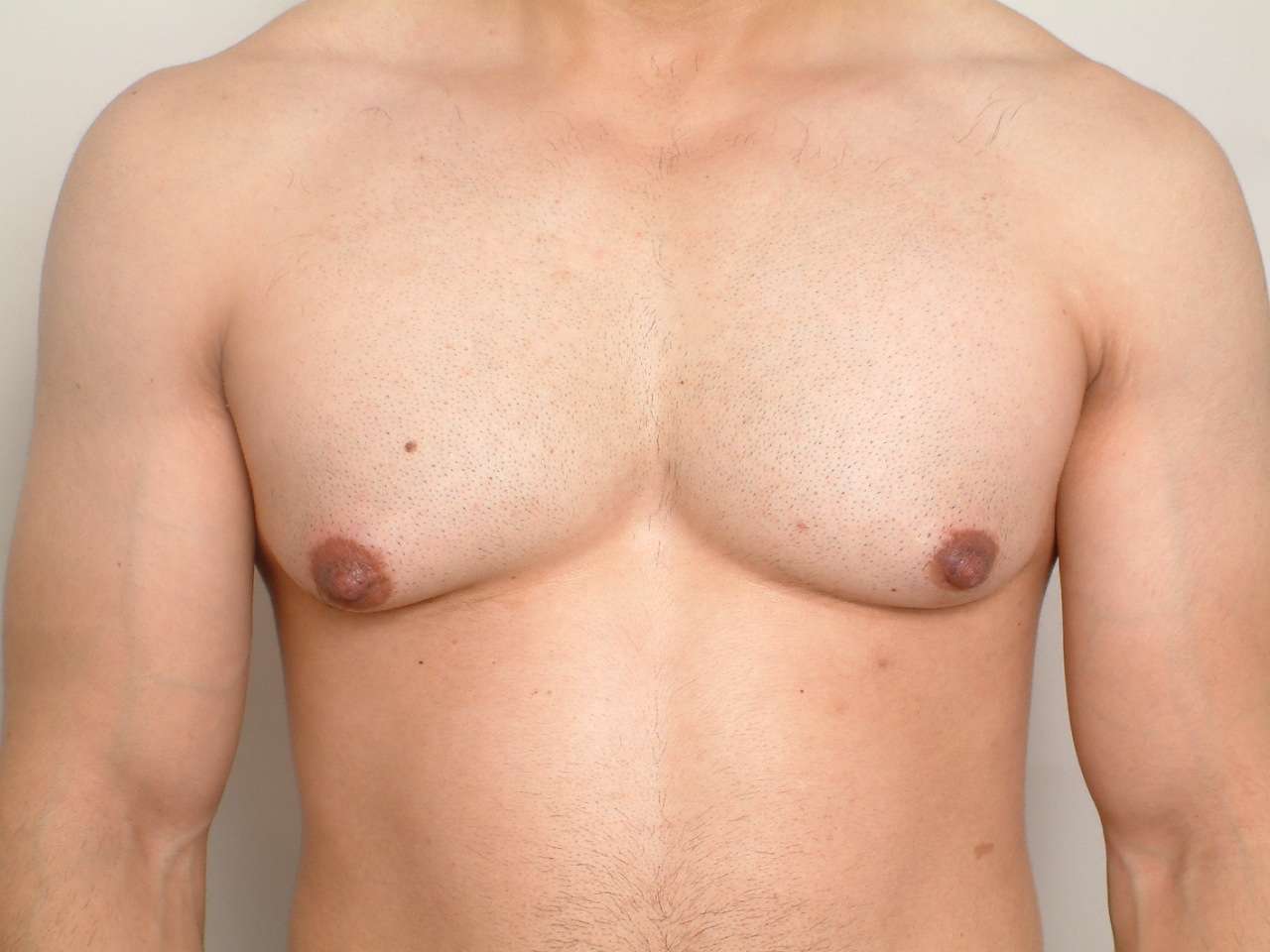
Gynecomastia is a condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males, causing the breasts to appear larger than normal. The symptoms of gynecomastia may include:
- Swollen or enlarged breast tissue: The most common symptom of gynecomastia is the enlargement of breast tissue in males. This may occur in one or both breasts.
- Tenderness or pain: Some individuals with gynecomastia may experience tenderness or pain in the breast tissue.
- Changes in breast appearance: Gynecomastia may cause changes in the appearance of the breast, such as a firm or rubbery texture, or an increase in the size of the areola (the darker area surrounding the nipple).
- Imbalance in breast size: In some cases, gynecomastia may cause one breast to be larger than the other, leading to an asymmetrical appearance.
- Psychological symptoms: Enlarged breasts in males can cause emotional distress, embarrassment, or self-consciousness, leading to psychological symptoms such as anxiety, depression, or body image issues.
It’s important to note that gynecomastia can be caused by a variety of factors, including hormonal changes, certain medications, obesity, underlying medical conditions, or genetic predisposition. In some cases, gynecomastia may resolve on its own, while in other cases, medical evaluation and treatment may be necessary.
If you are experiencing symptoms of gynecomastia or have concerns about changes in your breast tissue, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and diagnosis. Treatment options for gynecomastia may include medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery, depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
What are the causes of gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is caused by an imbalance of the hormones estrogen and testosterone, resulting in the development of enlarged breast tissue in males. Several factors can contribute to this hormonal imbalance and lead to the development of gynecomastia. Some common causes of gynecomastia include:
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes during puberty are a common cause of gynecomastia, as fluctuating levels of estrogen and testosterone can lead to the growth of breast tissue in males.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as anabolic steroids, anti-androgens, anti-anxiety medications, antidepressants, and drugs used to treat prostate cancer or heart conditions, may cause hormonal imbalances that result in gynecomastia.
- Health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as liver disease, kidney failure, hyperthyroidism, hypogonadism, and tumors of the pituitary gland or adrenal glands, can disrupt hormone levels and contribute to gynecomastia.
- Obesity: Excess body fat can lead to increased levels of estrogen production in males, contributing to the development of gynecomastia.
- Aging: As males age, the balance of hormones in the body can shift, leading to changes in breast tissue and an increased risk of gynecomastia.
- Genetic factors: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to gynecomastia, making them more susceptible to developing the condition.
- Substance abuse: The use of alcohol, marijuana, amphetamines, or other substances can disrupt hormone levels and contribute to the development of gynecomastia.
It’s important to note that gynecomastia can occur as a result of a combination of these factors, and the underlying cause of gynecomastia may vary from person to person. If you are experiencing symptoms of gynecomastia, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and diagnosis. Treatment options for gynecomastia may include addressing the underlying cause, making lifestyle changes, or considering medication or surgery, depending on the severity of the condition.
What is the treatment for gynecomastia?
The treatment for gynecomastia depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some treatment options for gynecomastia include:
- Observation: In some cases, gynecomastia may resolve on its own without the need for medical intervention. Your healthcare provider may recommend monitoring the condition to see if it improves over time.
- Medications: If gynecomastia is caused by hormonal imbalances, certain medications may be prescribed to help regulate hormone levels and reduce breast tissue growth. These medications may include selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) or aromatase inhibitors.
- Lifestyle changes: Making lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and reducing alcohol or substance use, can help improve hormonal balance and reduce the symptoms of gynecomastia.
- Surgical intervention: In cases where gynecomastia is severe or persistent, surgical procedures such as liposuction or breast reduction surgery may be recommended to remove excess breast tissue and improve the appearance of the chest.
- Psychological support: Gynecomastia can cause emotional distress and impact self-esteem. Counseling or support groups may be beneficial for individuals struggling with body image issues related to gynecomastia.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider or specialist if you are experiencing symptoms of gynecomastia to determine the appropriate treatment plan for your individual situation. Treatment options may vary depending on the underlying cause of gynecomastia, your overall health, and your personal preferences.