Abscessed Tooth: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of an abscessed tooth?
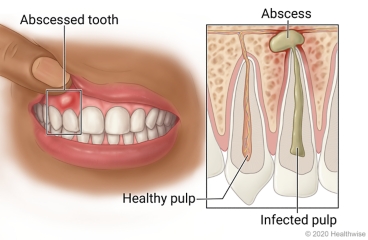
An abscessed tooth is a painful infection at the root of a tooth or between the tooth and the gum. It is typically caused by severe tooth decay, trauma to the tooth, or gum disease. The symptoms of an abscessed tooth can vary in severity but may include:
- Severe, throbbing toothache: The most common symptom of an abscessed tooth is a severe, persistent toothache that may radiate to the jawbone, neck, or ear on the same side of the face as the affected tooth.
- Pain when chewing or biting: Pain may increase when pressure is applied to the tooth, such as when chewing or biting down.
- Sensitivity to hot and cold: The affected tooth may be sensitive to hot or cold temperatures.
- Swelling in the face or cheek: Swelling in the face or cheek near the affected tooth may occur, and the area may feel tender to the touch.
- Fever: A low-grade fever may develop as the body’s immune system responds to the infection.
- Swollen lymph nodes: The lymph nodes in the neck may become swollen and tender.
- Pus drainage: If the abscess ruptures, pus may drain from the affected tooth, resulting in a foul taste in the mouth and relief from pain and pressure.
- Bad breath: An unpleasant taste or odor in the mouth may be present due to the infection.
- General discomfort or uneasiness: Some individuals may experience a general feeling of discomfort or uneasiness, often accompanied by fatigue.
It’s important to note that symptoms of an abscessed tooth can vary, and not all individuals may experience all of these symptoms. If you suspect you have an abscessed tooth, it’s important to see a dentist promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment. Without treatment, an abscessed tooth can lead to serious complications, including the spread of infection to other parts of the body.
What are the causes of an abscessed tooth?
An abscessed tooth is typically caused by a bacterial infection that occurs when a tooth’s inner pulp, which contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue, becomes infected. The infection can occur as a result of severe tooth decay, trauma to the tooth, or gum disease. Some common causes of an abscessed tooth include:
- Severe tooth decay: Tooth decay occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the enamel and dentin of the tooth, leading to the formation of a cavity. If left untreated, the decay can progress to the inner pulp of the tooth, leading to infection and abscess formation.
- Trauma to the tooth: Trauma to the tooth, such as a chip, crack, or fracture, can expose the inner pulp to bacteria, leading to infection and abscess formation.
- Gum disease: Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection of the gums and tissues that support the teeth. Advanced gum disease can lead to the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums where bacteria can accumulate and cause an abscess.
- Poor dental hygiene: Poor dental hygiene, including infrequent brushing and flossing, can lead to the buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth, increasing the risk of tooth decay and gum disease.
- Weakened immune system: A weakened immune system due to conditions such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or cancer can increase the risk of developing an abscessed tooth.
- Age: Older adults are at higher risk of developing abscessed teeth due to factors such as gum recession and a higher likelihood of having untreated cavities.
- Dry mouth: A lack of saliva can increase the risk of tooth decay and gum disease, leading to an increased risk of developing an abscessed tooth.
It’s important to practice good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, and to see a dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings to help prevent tooth decay and gum disease, which can lead to an abscessed tooth.
What is the treatment for an abscessed tooth?
The treatment for an abscessed tooth aims to eliminate the infection, alleviate pain, and prevent complications. The specific treatment approach may vary depending on the severity of the infection and the extent of damage to the tooth and surrounding tissues. Common treatments for an abscessed tooth include:
- Drainage of the abscess: If there is a visible abscess, your dentist may make an incision to drain the pus and relieve pressure. This can help alleviate pain and promote healing.
- Root canal therapy: If the infection has reached the pulp of the tooth, root canal therapy may be recommended. During this procedure, the infected pulp is removed, the root canal is cleaned and disinfected, and the tooth is filled and sealed.
- Antibiotics: If the infection is severe or has spread to other parts of the mouth or body, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help eliminate the infection. Antibiotics are typically used in conjunction with other treatments and are not usually sufficient on their own to treat an abscessed tooth.
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may be recommended to help alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Warm saltwater rinses: Rinsing with warm saltwater several times a day can help reduce swelling and pain.
- Dental crown: In some cases, a dental crown may be placed over the tooth after root canal therapy to protect and strengthen it.
- Tooth extraction: If the tooth is severely damaged and cannot be saved, extraction may be necessary to prevent the spread of infection to other teeth or parts of the mouth.
- Dental cleaning: In cases where gum disease is a contributing factor, a professional dental cleaning may be recommended to remove plaque and tartar buildup.
It’s important to see a dentist promptly if you suspect you have an abscessed tooth. Without treatment, an abscessed tooth can lead to serious complications, including the spread of infection to other parts of the body. A dentist can determine the best course of treatment based on your individual needs and the severity of your condition.
TL;DR: Abscessed Tooth Summary
An abscessed tooth, also known as a dental abscess, is a painful dental condition characterized by a buildup of pus within the tooth or the surrounding gums. It is typically caused by a bacterial infection and can result from untreated tooth decay, gum disease, or dental trauma. Abscessed teeth can lead to severe pain, swelling, and other complications if left untreated.
Symptoms of an abscessed tooth may include:
- Severe, throbbing toothache
- Swelling in the face or around the affected tooth
- Fever
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck or jaw
- Foul-tasting drainage from the infected tooth or gums
- Difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing
- General discomfort or malaise
If you suspect you have an abscessed tooth, it is essential to seek prompt dental treatment to prevent the infection from spreading and causing further complications. A dentist can diagnose an abscessed tooth through a physical examination, dental X-rays, and possibly other diagnostic tests.
Treatment for an abscessed tooth may involve:
- Draining the abscess: The dentist may drain the pus buildup through a small incision to relieve pain and pressure.
- Root canal treatment: If the infection has reached the pulp of the tooth, a root canal procedure may be necessary to remove the infected tissue and seal the tooth.
- Antibiotics: In cases of severe infection or if the infection has spread, antibiotics may be prescribed.
- Tooth extraction: In some cases, the affected tooth may need to be extracted if it cannot be saved.
It is crucial to practice good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, to prevent tooth decay and gum disease that can lead to abscessed teeth. If you experience severe tooth pain, swelling, or other symptoms of an abscessed tooth, do not delay seeking dental care to prevent further complications and alleviate discomfort.