Asthma: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms & triggers of asthma?
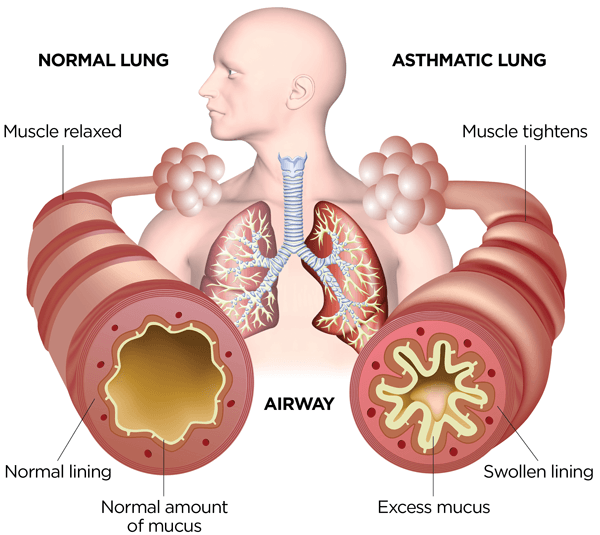
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways. The symptoms of asthma can vary in severity and frequency, and they may include the following:
- Shortness of breath: One of the most common symptoms of asthma is difficulty breathing or a feeling of tightness in the chest, especially during physical activity or when exposed to triggers.
- Wheezing: A whistling or wheezing sound when exhaling, caused by the constricted airways.
- Coughing: Asthma can cause persistent coughing, especially at night or early morning. The cough may be dry or accompanied by mucus production.
- Chest tightness or pain: Some people with asthma experience a feeling of tightness or discomfort in the chest area.
- Rapid breathing: Asthma can cause rapid, shallow breathing, especially during an asthma attack.
- Difficulty speaking: During an asthma attack, the inability to breathe deeply can make it challenging to speak in full sentences.
- Fatigue: The extra effort required for breathing can lead to tiredness and fatigue.
- Anxiety or panic: The struggle to breathe can trigger feelings of anxiety or panic, especially during severe asthma attacks.
The symptoms of asthma can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Allergens (e.g., pollen, dust mites, pet dander)
- Respiratory infections (e.g., colds, flu)
- Exercise or physical activity
- Cold air
- Airborne irritants (e.g., smoke, strong odors)
- Stress or emotional factors
It’s important to note that not all individuals with asthma experience the same symptoms, and the severity can vary from person to person. Some people may have mild, infrequent symptoms, while others may experience more persistent and severe asthma attacks. Proper diagnosis and management by a healthcare provider of asthma are crucial to control symptoms and prevent potentially life-threatening exacerbations.
What are the causes of asthma?
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by recurring episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. The causes of asthma are complex and multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. Here are some of the main causes of asthma:
- Genetic predisposition: Asthma can be inherited, and individuals with a family history of asthma are more likely to develop the disease.
- Allergies: Allergies to substances such as pollen, dust mites, mold, and pet dander can trigger asthma symptoms.
- Airway inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the airways can cause the airways to become sensitive and narrow, leading to symptoms of asthma.
- Respiratory infections: Respiratory infections such as bronchitis, pneumonia, and sinusitis can trigger asthma symptoms.
- Exposure to environmental irritants: Exposure to environmental irritants such as tobacco smoke, air pollution, and chemicals can trigger asthma symptoms.
- Occupational exposures: Certain occupations such as manufacturing, construction, and mining can expose individuals to substances that trigger asthma symptoms.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes during puberty, menopause, or pregnancy can trigger asthma symptoms.
- Obesity: Obesity is a risk factor for developing asthma, particularly in children.
- Smoking: Smoking is a risk factor for developing asthma, particularly in adults.
- Other medical conditions: Certain medical conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), sleep apnea, and sinusitis can increase the risk of developing asthma.
It’s important to note that not everyone with these risk factors will develop asthma, and many people with asthma do not have any obvious risk factors. Additionally, the exact causes of asthma are still not fully understood and may involve a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors.
What is the treatment for asthma?
The treatment for asthma typically involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and avoidance of triggers. The goal of treatment is to control symptoms, prevent exacerbations, and improve lung function. Here are some common treatments for asthma:
- Medications:
- Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) to reduce inflammation and prevent symptoms.
- Quick-relief medications such as bronchodilators (e.g., albuterol) to relieve symptoms during an asthma attack.
- Long-acting beta2 agonists (LABA) to help control symptoms and prevent attacks.
- Combination inhalers that contain both ICS and LABA.
- Oral corticosteroids (OCS) for severe asthma attacks.
- Lifestyle changes:
- Avoiding triggers such as allergens, tobacco smoke, and air pollution.
- Identifying and avoiding specific triggers that can cause symptoms.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce the risk of developing asthma.
- Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke.
- Lung function testing: Regular lung function tests (spirometry) to monitor lung function and adjust treatment as needed.
- Peak flow monitoring: Monitoring peak flow rates to track lung function and detect early signs of worsening asthma.
- Asthma action plan: Creating a personalized asthma action plan with your healthcare provider to help manage symptoms and prevent exacerbations.
In addition to these treatments, there are also some alternative therapies that may be helpful in managing asthma symptoms, such as:
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture has been shown to improve lung function and reduce symptoms in people with asthma.
- Yoga: Yoga has been shown to improve lung function and reduce symptoms in people with asthma.
- Breathing exercises: Breathing exercises such as diaphragmatic breathing can help improve lung function and reduce symptoms in people with asthma.
It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs and symptoms.