Blepharitis: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of blepharitis?
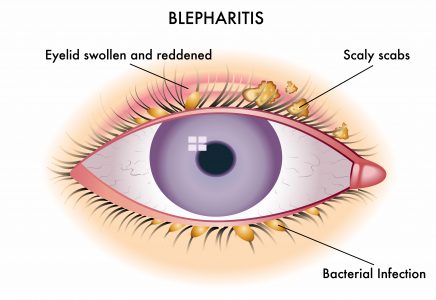
Blepharitis is a common and chronic condition that causes inflammation of the eyelids. The symptoms of blepharitis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, but common symptoms may include:
- Redness and swelling of the eyelids
- Itching or burning sensation in the eyes
- Gritty or foreign body sensation in the eyes
- Excessive tearing or watering of the eyes
- Crusting or flakes on the eyelids or eyelashes
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Blurred or fluctuating vision
- Swollen and/or greasy eyelids
- Loss of eyelashes or misdirected growth of eyelashes (distichiasis)
- Difficulty wearing contact lenses
Blepharitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacterial or fungal infections, skin conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis or rosacea, and dysfunction of the oil glands in the eyelids. Treatment for blepharitis may involve cleansing the eyelids with warm compresses, gentle eyelid scrubs, and eyelid hygiene products, as well as managing any underlying conditions contributing to the inflammation.
It is important to see an eye care professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan if you are experiencing symptoms of blepharitis. Prompt and proper management of blepharitis can help relieve symptoms, improve eye comfort, and reduce the risk of complications.
What are the causes of blepharitis?
Blepharitis is a common and chronic condition characterized by inflammation of the eyelids. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Bacterial overgrowth: One of the most common causes of blepharitis is an overgrowth of bacteria on the eyelids. These bacteria can contribute to inflammation and irritation of the eyelid margins.
- Meibomian gland dysfunction: Dysfunction of the meibomian glands, which are the oil glands located along the eyelid margins, can lead to blepharitis. When the meibomian glands become blocked or produce abnormal oil, it can affect the quality of the tear film and lead to inflammation.
- Skin conditions: Certain skin conditions, such as seborrheic dermatitis and rosacea, can also contribute to blepharitis. These conditions can cause inflammation of the skin, including the eyelids, and may lead to irritation and crusting.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to substances such as makeup, eye drops, or contact lens solutions can trigger inflammation of the eyelids and contribute to blepharitis.
- Demodex mites: Infestation of the eyelids with Demodex mites, which are microscopic parasites that naturally live in the hair follicles, can also be a contributing factor to blepharitis. These mites can cause inflammation and irritation of the eyelids.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors such as air pollution, smoke, and exposure to allergens can worsen symptoms of blepharitis for some individuals.
- Poor eyelid hygiene: Not maintaining proper eyelid hygiene, such as failure to regularly clean the eyelids, can increase the risk of developing blepharitis.
It’s important to see an eye care professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan if you suspect you may have blepharitis. Identifying the underlying cause of blepharitis is essential for effective management and symptom relief. Proper eyelid hygiene, regular eye exams, and appropriate treatment can help control symptoms and reduce the frequency of flare-ups of blepharitis.
What is the treatment for blepharitis?
The treatment for blepharitis typically involves a combination of home care practices and medical interventions tailored to address the underlying cause of the condition. Some common treatment options for blepharitis include:
- Warm compresses: Applying warm compresses to the eyelids can help soften oil secretions, open up blocked glands, and reduce inflammation. This can improve eyelid hygiene and alleviate symptoms of blepharitis.
- Lid scrubs: Using gentle eyelid cleansers or lid scrubs can help remove debris, crusting, and bacteria from the eyelids. This can help reduce inflammation and prevent recurrence of blepharitis.
- Eye drops or ointments: In cases where inflammation or dry eye symptoms are present, prescription or over-the-counter eye drops or ointments may be recommended to relieve discomfort and improve tear film stability.
- Antibiotics: In cases of bacterial blepharitis, antibiotic ointments, drops, or oral antibiotics may be prescribed to help reduce bacterial overgrowth and inflammation.
- Steroid eye drops: In cases of severe inflammation, steroid eye drops may be prescribed for short-term use to reduce swelling and irritation.
- Meibomian gland expression: For patients with meibomian gland dysfunction, manual expression of the blocked oil glands may be performed by a healthcare provider to improve gland function and relieve symptoms.
- Demodex treatments: If Demodex mites are identified as a contributing factor, treatments targeting the mites, such as tea tree oil-based products or medicated cleansers, may be recommended.
- Lifestyle modifications: Making changes to your lifestyle, such as improving eyelid hygiene, avoiding irritants, and managing underlying skin conditions like rosacea, can help prevent flare-ups of blepharitis.
It’s important to work closely with your eye care provider to create an individualized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and symptoms. Consistent eyelid hygiene practices, regular follow-up appointments, and adherence to prescribed treatments are key to managing blepharitis and improving eye comfort and health.