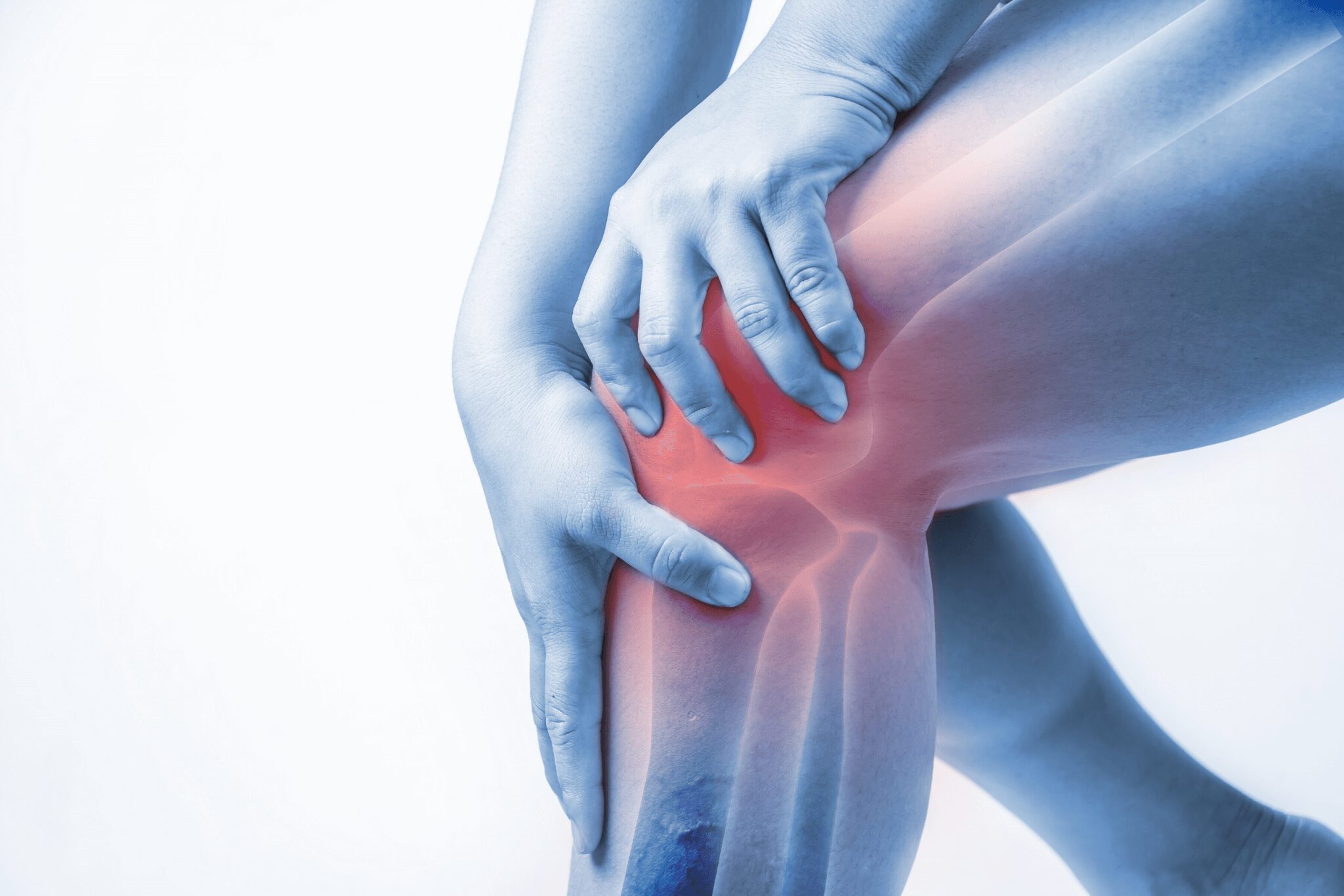
Bursitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
What are the symptoms of bursitis?
The main symptoms of bursitis include:
- Joint pain: This is the primary symptom. The pain is usually worsened with movement or pressure over the affected bursa.
- Swelling: The bursa, which is a small fluid-filled sac near the joint, can swell up and cause a visibly swollen area.
- Warmth: The affected area may feel warmer to the touch due to inflammation.
- Stiffness: Moving the joint or limb may be difficult and stiff, especially after periods of inactivity.
- Tenderness: The area around the inflamed bursa is usually very tender to the touch.
- Limited range of motion: When the bursa is inflamed, it can restrict the normal range of motion in that joint.
- Redness: In some cases, the skin over the inflamed bursa may appear reddened.
- Limping: If bursitis affects a joint in the leg or hip, it may cause a limp when walking.
The most commonly affected areas for bursitis are the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees. Symptoms may start gradually or come on suddenly, especially after trauma or repetitive motion to the area. Proper treatment from a competent healthcare provider can help relieve pain and swelling.
What are the causes of bursitis?
There are several potential causes of bursitis:
- Repetitive motion – Repeated minor impacts or movements over time can irritate and inflame the bursa sacs. This is common in jobs or activities that involve repetitive motions like throwing, lifting, or kneeling.
- Injury/Trauma – A direct blow or injury to an area near a bursa can cause inflammation and bursitis. This can happen from a fall, bump, or sudden twisting motion.
- Incorrect posture – Poor posture that compresses a bursa over long periods, like leaning on elbows or crossing legs, can lead to bursitis.
- Bone spurs/Calcium deposits – Bony protrusions or calcium deposits near a bursa can rub against it and cause chronic inflammation.
- Arthritis – Inflammatory forms of arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis can increase the risk of developing bursitis.
- Infection – In rare cases, a bacterial infection can occur inside a bursa sac, causing infectious bursitis.
- Metabolic disorders – Certain conditions like gout or thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism may increase the risk.
- Overuse – Activities that overwork a joint like running long distances can overuse the bursa.
- Age – The bursa sacs can become less elastic with age, making them more prone to irritation.
Some of the most commonly affected areas are the shoulders, hips, knees and elbows due to their joint movements and likelihood of sustained pressure or repetitive motions.
What is the treatment for bursitis?
The treatment for bursitis typically involves a combination of the following approaches:
- Rest and Activity Modification
Resting the affected joint and avoiding activities that aggravate the bursitis is important initially. This allows the inflamed bursa to heal. - Ice Application
Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce pain and swelling. - Medication
Anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen or naproxen can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Cortisone injections into the inflamed bursa may also be used for severe cases. - Physical Therapy
Specific stretches and exercises can help maintain range of motion and strengthen the muscles around the affected joint once the initial inflammation subsides. - Assistive Devices
Using crutches, canes or splints to avoid putting pressure on the inflamed area during recovery can be helpful. - Supplements
Supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin may help reduce inflammation and pain associated with bursitis. - Bursa Drainage/Removal
For chronic or recurrent bursitis that doesn’t improve, draining the excess fluid from the inflamed bursa or surgically removing the bursa may be recommended. - Antibiotics
If the bursitis is caused by an infection, oral antibiotics will be prescribed to treat it. - Injections
Steroid injections into the inflamed bursa can provide longer-term relief in some cases.
Getting proper treatment, modifying activities to avoid re-injury, and doing prescribed exercises are important for recovering from bursitis fully.