Cold Sores: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
What are the symptoms of a cold sore?
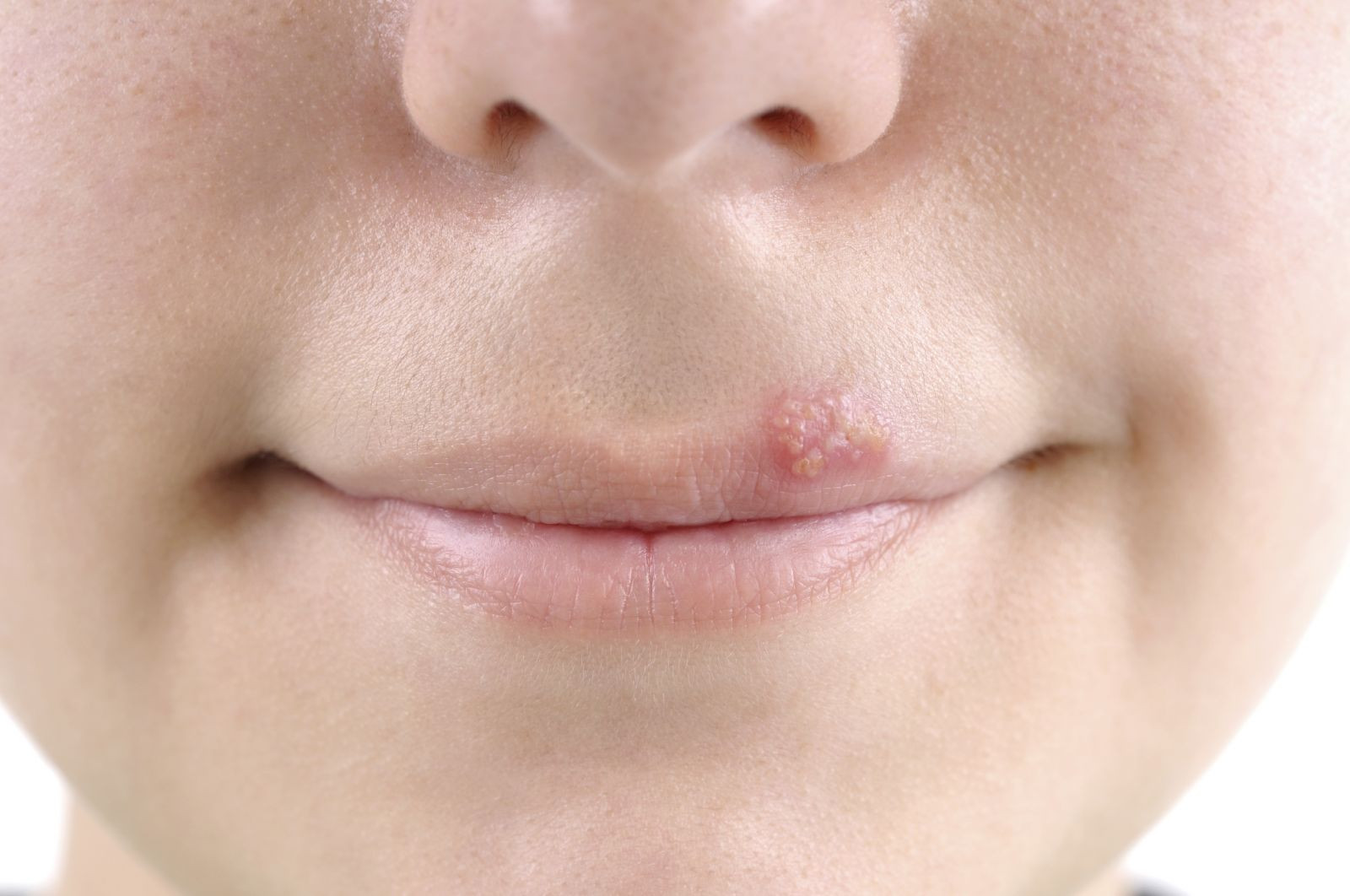
Cold sores, also known as fever blisters, are small, fluid-filled blisters that typically appear on or around the lips. They are caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) and are highly contagious. The symptoms of a cold sore can vary but may include:
- Tingling or itching: A few days before a cold sore appears, you may feel tingling, itching, or burning in the area where the sore will develop.
- Small, fluid-filled blisters: Cold sores usually appear as small, fluid-filled blisters on or around the lips. The blisters may be grouped together in a cluster or may occur singly.
- Pain or discomfort: Cold sores can be painful or tender to the touch, especially when the blisters break open and leak fluid.
- Crusting: After a few days, the blisters may break open and form a crust or scab. The crust will eventually dry up and fall off, revealing new skin underneath.
- Swelling and redness: The skin around the cold sore may become swollen and red.
- Fever and swollen lymph nodes: Some people may experience fever, swollen lymph nodes, and general malaise when they have a cold sore outbreak.
Cold sores usually heal on their own within 7 to 10 days. However, the virus remains in the body and can cause recurrent outbreaks in the future, especially during times of stress, illness, or sun exposure. There is no cure for the herpes simplex virus, but antiviral medications can help reduce the severity and duration of cold sore outbreaks.
What are the causes of a cold sore?
Cold sores are caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), specifically HSV-1. HSV-1 is highly contagious and is typically transmitted through close contact with an infected person. The virus is most commonly spread through:
- Direct contact: Cold sores are most contagious when the blisters are oozing fluid. Direct contact with the fluid from a cold sore can spread the virus to another person.
- Indirect contact: The virus can also be spread through indirect contact, such as sharing utensils, towels, or other items with an infected person.
- Kissing: Kissing an infected person, especially when they have an active cold sore, can transmit the virus.
- Oral sex: HSV-1 can also be transmitted through oral-genital contact, leading to genital herpes.
Once a person is infected with HSV-1, the virus remains in the body and can become dormant in nerve cells near the ear. Periodically, the virus can reactivate, traveling back to the skin surface and causing a new outbreak of cold sores. Reactivations can be triggered by various factors, including stress, illness, sun exposure, hormonal changes, and weakened immune system.
It’s important to note that while HSV-1 is the most common cause of cold sores, HSV-2, which is typically associated with genital herpes, can also cause cold sores through oral-genital contact.
What is the treatment for a cold sore?
The treatment for a cold sore can help reduce the severity of symptoms and speed up the healing process. Some common treatments for cold sores include:
- Antiviral medications: Over-the-counter (OTC) antiviral creams, such as docosanol (Abreva), can help reduce the duration and severity of a cold sore outbreak if applied at the first sign of symptoms. Prescription antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, are also available and may be more effective in some cases.
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help relieve pain and discomfort associated with cold sores.
- Topical treatments: Some people find relief from topical treatments, such as lidocaine or benzocaine, which can help numb the affected area and reduce pain.
- Moisturizing creams: Applying a moisturizing cream or lip balm can help keep the affected area moist and prevent cracking.
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers that can cause cold sore outbreaks, such as stress, illness, or sun exposure, can help prevent future outbreaks.
It’s important to start treatment as soon as you notice symptoms of a cold sore, such as tingling or itching, to help reduce the severity and duration of the outbreak. If you have frequent or severe cold sore outbreaks, talk to your healthcare provider about prescription antiviral medications or other treatment options.