Crabs (Pubic Lice): Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of pubic lice?
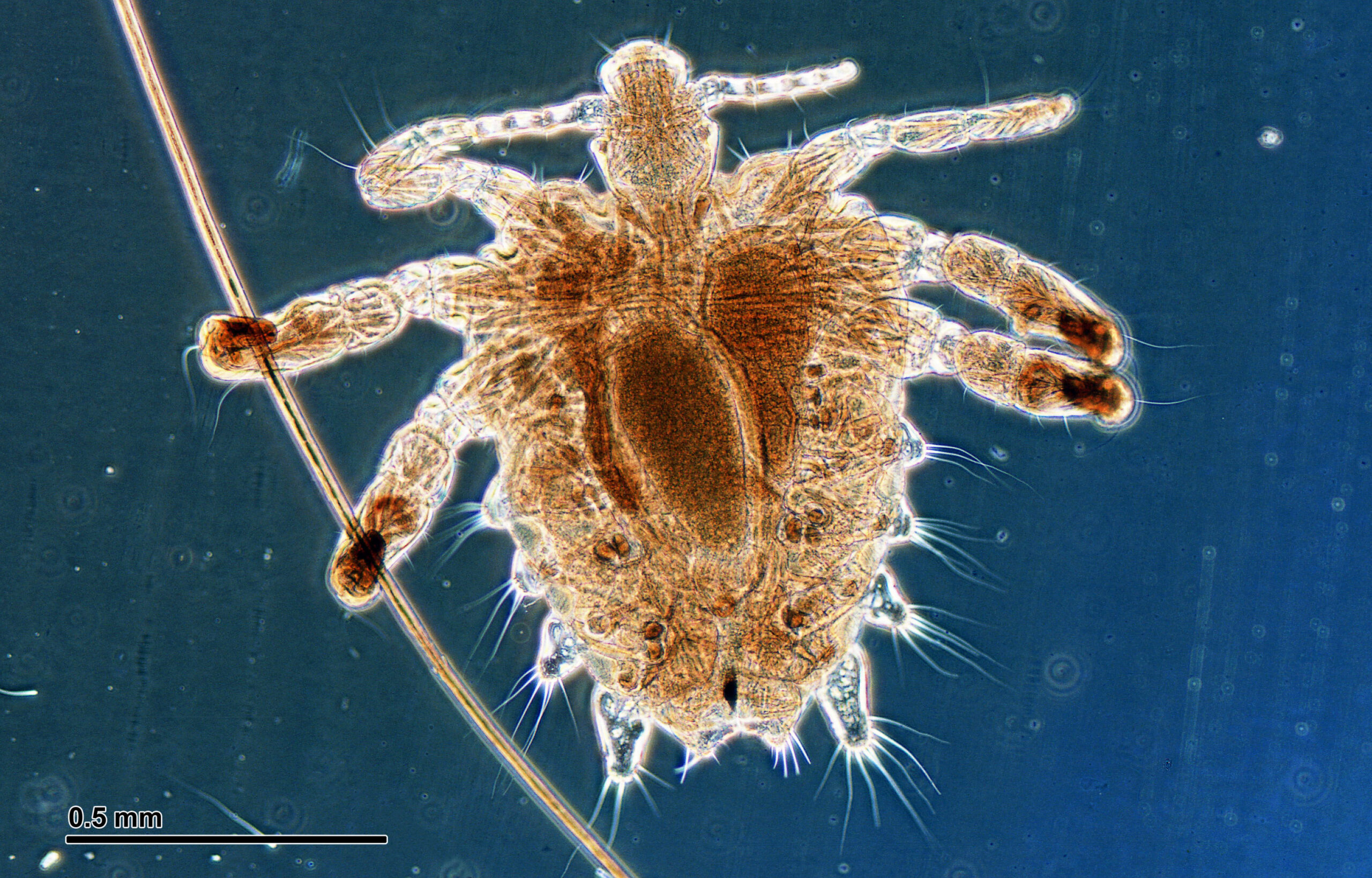
Pubic lice, also known as “crabs,” are small parasitic insects that infest the pubic hair area and feed on blood. The symptoms of pubic lice infestation may include:
- Itching: Intense itching in the pubic hair area is a common symptom of pubic lice infestation. The itching is caused by an allergic reaction to the lice bites.
- Visible lice: Adult pubic lice are tiny insects that are visible to the naked eye. They are typically about the size of a pinhead and have a crab-like appearance, which is how they get their nickname.
- Nits: Nits are the eggs of pubic lice and may appear as tiny white or yellow dots attached to the hair shafts near the skin. Nits are often easier to spot than adult lice.
- Skin irritation: The bites of pubic lice can cause skin irritation, redness, and inflammation in the affected area.
- Blue spots or spots of blood: Sometimes, small blue spots or spots of blood may be visible on the skin where the lice have bitten.
- Feeling of movement: Some people with pubic lice infestations may feel a sensation of movement in the pubic hair area, although this is less common.
It’s important to note that pubic lice infestations are usually spread through close personal contact, such as sexual contact. If you suspect that you have pubic lice, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Pubic lice infestations can usually be treated with over-the-counter or prescription medications that kill the lice and their eggs.
What are the causes of pubic lice?
Pubic lice are typically spread through close personal contact, such as sexual contact. However, they can also be spread through infested clothing, towels, or bedding. The main causes of pubic lice infestations include:
- Sexual contact: Pubic lice are most commonly spread through sexual contact with an infected person. This can include vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
- Close personal contact: Pubic lice can also be spread through close personal contact with an infected person, such as sharing clothing, towels, or bedding.
- Unhygienic conditions: While not a direct cause, unhygienic conditions can contribute to the spread of pubic lice. Infestations are more likely to occur in crowded or unclean environments.
It’s important to note that pubic lice infestations are not a sign of poor hygiene and can happen to anyone. Treatment for pubic lice typically involves using over-the-counter or prescription medications that kill the lice and their eggs. It’s also important to wash infested clothing, towels, and bedding in hot water to help prevent the spread of lice to others.
What is the treatment for pubic lice?
The treatment for pubic lice, also known as “crabs,” typically involves using medicated products that kill the lice and their eggs (nits). The most common treatments for pubic lice infestations include:
- Over-the-counter (OTC) lotions or shampoos: Products containing permethrin or pyrethrin are commonly used to treat pubic lice. These products are applied to the affected area and left on for a specified period of time before being washed off. It may be necessary to repeat the treatment after one week to kill any newly hatched lice.
- Prescription medications: In some cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe a stronger medication, such as malathion or ivermectin, to treat pubic lice infestations that are resistant to OTC treatments.
- Manual removal: In addition to using medicated products, manual removal of lice and nits using a fine-toothed comb or tweezers may be necessary to completely eliminate the infestation.
- Washing infested clothing and bedding: It’s important to wash infested clothing, towels, and bedding in hot water and dry them on high heat to kill any lice or nits.
- Avoiding re-infestation: To prevent re-infestation, avoid close personal contact with infested individuals and wash any clothing, towels, or bedding that may have come into contact with lice.
It’s important to follow the instructions provided with the medication and to complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve. If you have pubic lice, it’s also important to inform any sexual partners so that they can be treated as well. If over-the-counter treatments are not effective, or if you have a severe infestation, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for further evaluation and treatment.