Folliculitis: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of folliculitis?
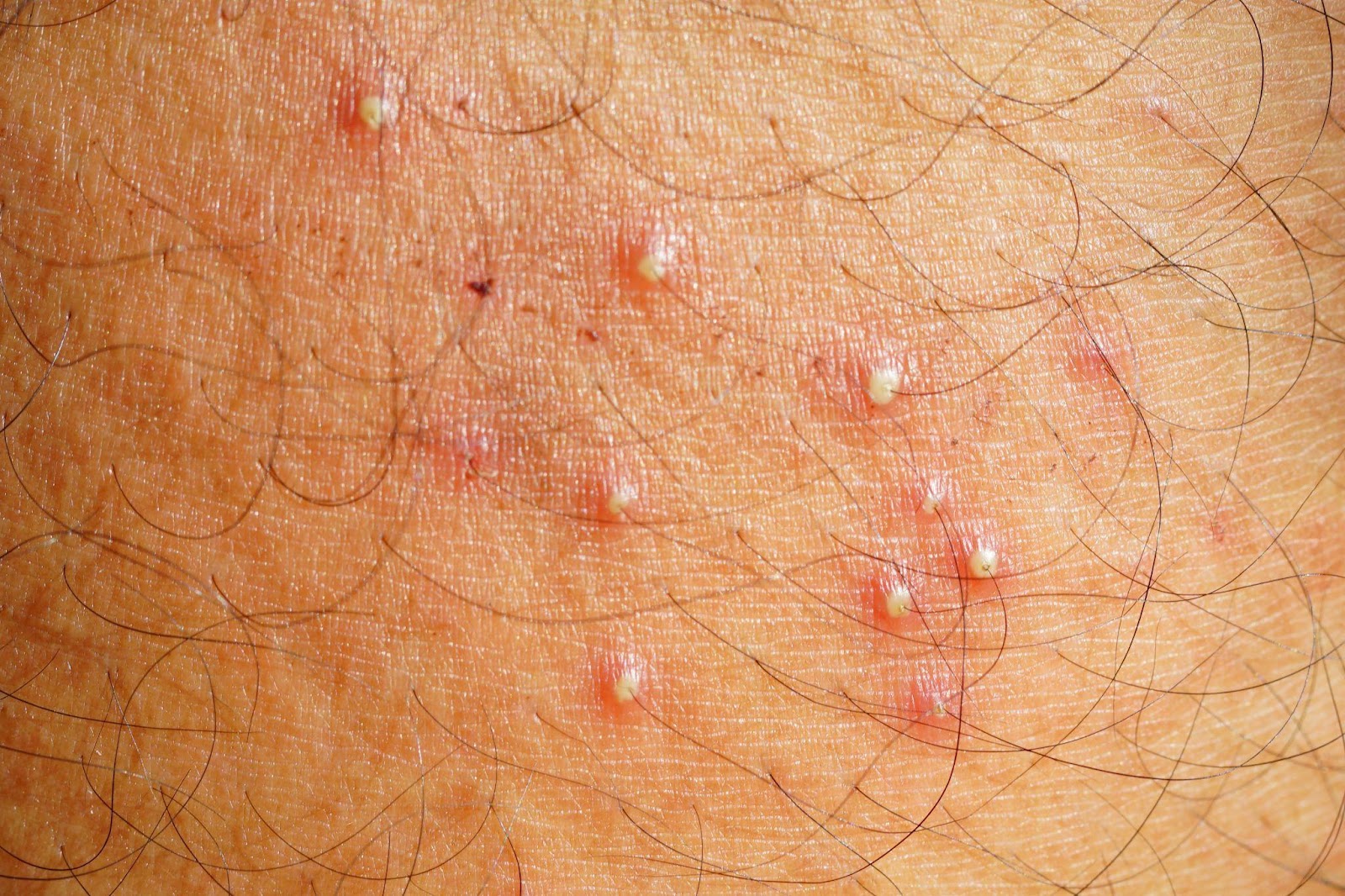
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become inflamed or infected. It can affect any part of the body where hair grows, including the scalp, face, neck, chest, back, buttocks, and legs. The symptoms of folliculitis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, but common symptoms may include:
- Red or Pimple-Like Bumps: Folliculitis often appears as small red or white bumps around hair follicles. These bumps may be itchy or tender.
- Pus-Filled Bumps: In more severe cases, the bumps may become filled with pus, which can be a sign of a bacterial infection.
- Itching or Burning: Folliculitis can cause itching, burning, or a tingling sensation in the affected area.
- Hair Loss: In some cases, folliculitis can lead to temporary hair loss in the affected area.
- Pain or Tenderness: The affected area may be painful or tender to the touch, especially if the folliculitis is caused by a bacterial infection.
- Scarring: Severe or recurrent folliculitis can lead to scarring, especially if the bumps are repeatedly irritated or scratched.
- Fever and Swelling: In rare cases, folliculitis can cause fever and swelling in the affected area, which may indicate a more serious infection.
Folliculitis can be acute, meaning it develops suddenly and resolves on its own, or chronic, meaning it persists or recurs over time. It can be caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses, or other factors that irritate or infect the hair follicles. Treatment for folliculitis depends on the underlying cause and may include topical or oral antibiotics, antifungal medications, or other treatments to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. If you suspect that you have folliculitis, you will need to discuss it with your dermatologist.
What are the causes of folliculitis?
Folliculitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Bacterial Infection: The most common cause of folliculitis is infection with bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus. Bacterial folliculitis can occur when bacteria enter the hair follicle through a cut, scrape, or other skin injury.
- Fungal Infection: Fungal infections, such as those caused by yeast or dermatophytes, can also cause folliculitis. These infections are more common in warm, moist environments.
- Viral Infection: Viral infections, such as herpes simplex virus or varicella-zoster virus, can sometimes lead to folliculitis.
- Ingrown Hairs: Ingrown hairs occur when hair curls back or grows sideways into the skin, leading to inflammation and folliculitis.
- Blockage of the Hair Follicle: Anything that blocks or irritates the hair follicle, such as tight clothing, shaving, or certain skin care products, can increase the risk of folliculitis.
- Skin Conditions: Certain skin conditions, such as acne or eczema, can increase the risk of developing folliculitis.
- Weakened Immune System: A weakened immune system, either due to an underlying medical condition or medications that suppress the immune system, can increase the risk of developing folliculitis.
- Chemicals and Irritants: Exposure to certain chemicals or irritants, such as oils, greases, or harsh detergents, can irritate the hair follicles and lead to folliculitis.
Folliculitis can occur anywhere on the body where hair grows. The condition is more common in areas where there is friction or sweating, such as the scalp, face, neck, chest, back, buttocks, and legs.
What is the treatment for folliculitis?
Treatment for folliculitis depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In many cases, mild cases of folliculitis may resolve on their own without treatment. However, if the condition is persistent, recurrent, or causes discomfort, treatment options may include:
- Antibiotics: If the folliculitis is caused by a bacterial infection, topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed to help clear the infection. Topical antibiotics are often used for mild cases, while oral antibiotics may be necessary for more severe or widespread infections.
- Antifungal Medications: If the folliculitis is caused by a fungal infection, antifungal medications, such as creams, lotions, or oral medications, may be prescribed to treat the infection.
- Topical Steroids: In cases where folliculitis is caused by inflammation, such as in eosinophilic folliculitis, topical steroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms.
- Antiviral Medications: If the folliculitis is caused by a viral infection, such as herpes simplex virus or varicella-zoster virus, antiviral medications may be prescribed to treat the infection.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected area can help soothe the skin and reduce inflammation.
- Avoiding Irritants: Avoiding factors that can irritate the skin, such as tight clothing, shaving, or harsh skin care products, may help prevent folliculitis from recurring.
- Good Skin Hygiene: Practicing good skin hygiene, such as keeping the skin clean and dry, can help prevent folliculitis and reduce the risk of recurrence.
In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend a culture or other tests to determine the underlying cause of folliculitis and guide treatment. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for treatment and to avoid picking or scratching the affected area, as this can lead to further irritation and infection. If you have recurrent or severe folliculitis, it’s a good idea to consult with a dermatologist for further evaluation and management.