Hirsutism: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of hirsutism?
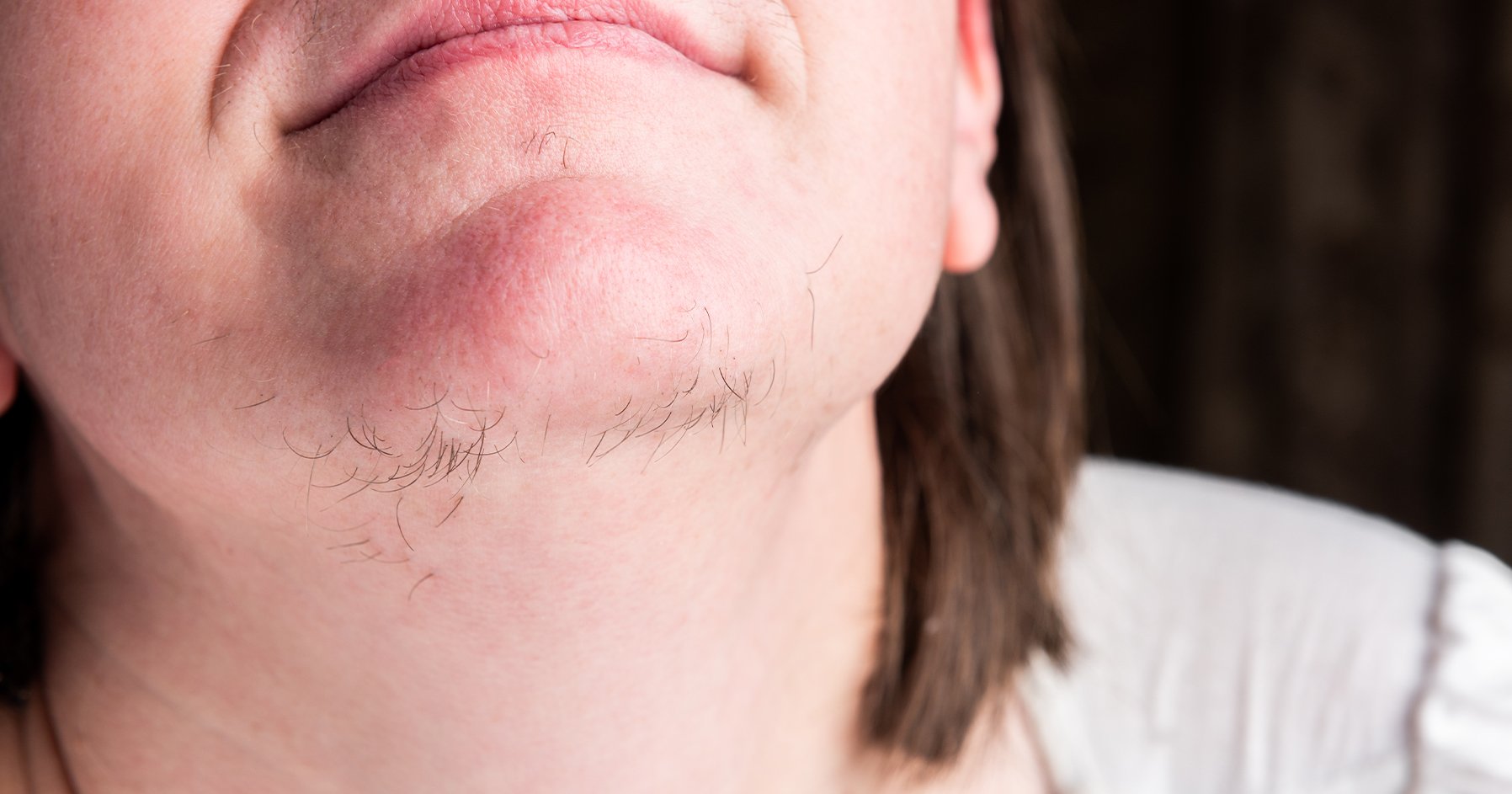
Hirsutism is a condition in which women experience excessive hair growth in areas where hair is normally minimal or absent, such as the face, chest, and back. Symptoms of hirsutism can vary but may include:
- Excessive hair growth: Women with hirsutism may develop coarse, dark hair in areas where men typically grow hair, such as the face (upper lip, chin), chest, back, and abdomen.
- Increased hair growth over time: The hair growth associated with hirsutism tends to worsen gradually over months or years.
- Thicker or darker hair: The hair that grows in areas affected by hirsutism may be thicker, darker, and more noticeable than normal body hair.
- Hair in unusual areas: Women with hirsutism may notice hair growth in areas where women typically do not have much hair, such as the upper lip, chin, and lower abdomen.
- Other signs of male-pattern hair growth: In addition to excessive facial and body hair, some women with hirsutism may also experience other signs of male-pattern hair growth, such as balding or thinning of the hair on the scalp.
It’s important to note that hirsutism can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or adrenal gland disorders. If you are experiencing symptoms of hirsutism, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
What are the causes of hirsutism?
Hirsutism is often caused by an excess of male hormones called androgens, specifically testosterone, in the female body. The condition can be caused by several factors, including:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age. It is characterized by high levels of androgens, irregular menstrual cycles, and small cysts in the ovaries. PCOS is a leading cause of hirsutism.
- Idiopathic hirsutism: In some cases, the exact cause of hirsutism cannot be determined. This is known as idiopathic hirsutism.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as anabolic steroids, corticosteroids, and some hormonal contraceptives, can cause hirsutism as a side effect.
- Adrenal gland disorders: Conditions that affect the adrenal glands, such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia and Cushing’s syndrome, can lead to hirsutism.
- Tumors: Rarely, tumors of the ovaries or adrenal glands can produce androgens and cause hirsutism.
- Family history: Hirsutism can run in families, suggesting a genetic component.
- Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance, which is common in women with PCOS, can also contribute to hirsutism.
It’s important to note that hirsutism can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. If you are experiencing symptoms of hirsutism, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
What is the treatment for hirsutism?
The treatment for hirsutism aims to reduce hair growth and manage any underlying conditions that may be causing the excess hair growth. Treatment options may include:
- Medications:
- Oral contraceptives: Birth control pills containing estrogen and progestin can help regulate hormonal imbalances and reduce androgen production.
- Anti-androgens: Medications such as spironolactone and finasteride can block the effects of androgens and reduce hair growth.
- Topical cream: Eflornithine cream can help slow the growth of facial hair in women.
- Hair removal methods:
- Shaving: Shaving can quickly remove hair, but it needs to be done regularly.
- Waxing or sugaring: These methods remove hair from the root and can provide longer-lasting results.
- Laser hair removal: This procedure uses laser light to destroy hair follicles, reducing hair growth over time.
- Electrolysis: This method uses an electric current to destroy hair follicles, leading to permanent hair removal.
- Managing underlying conditions: If hirsutism is caused by an underlying condition such as PCOS, treatment may focus on managing that condition to help reduce hair growth.
- Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and managing stress can help improve hormonal balance and reduce hair growth.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any treatment for hirsutism, as they can help determine the underlying cause and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.