Nail Fungus: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of nail fungus?
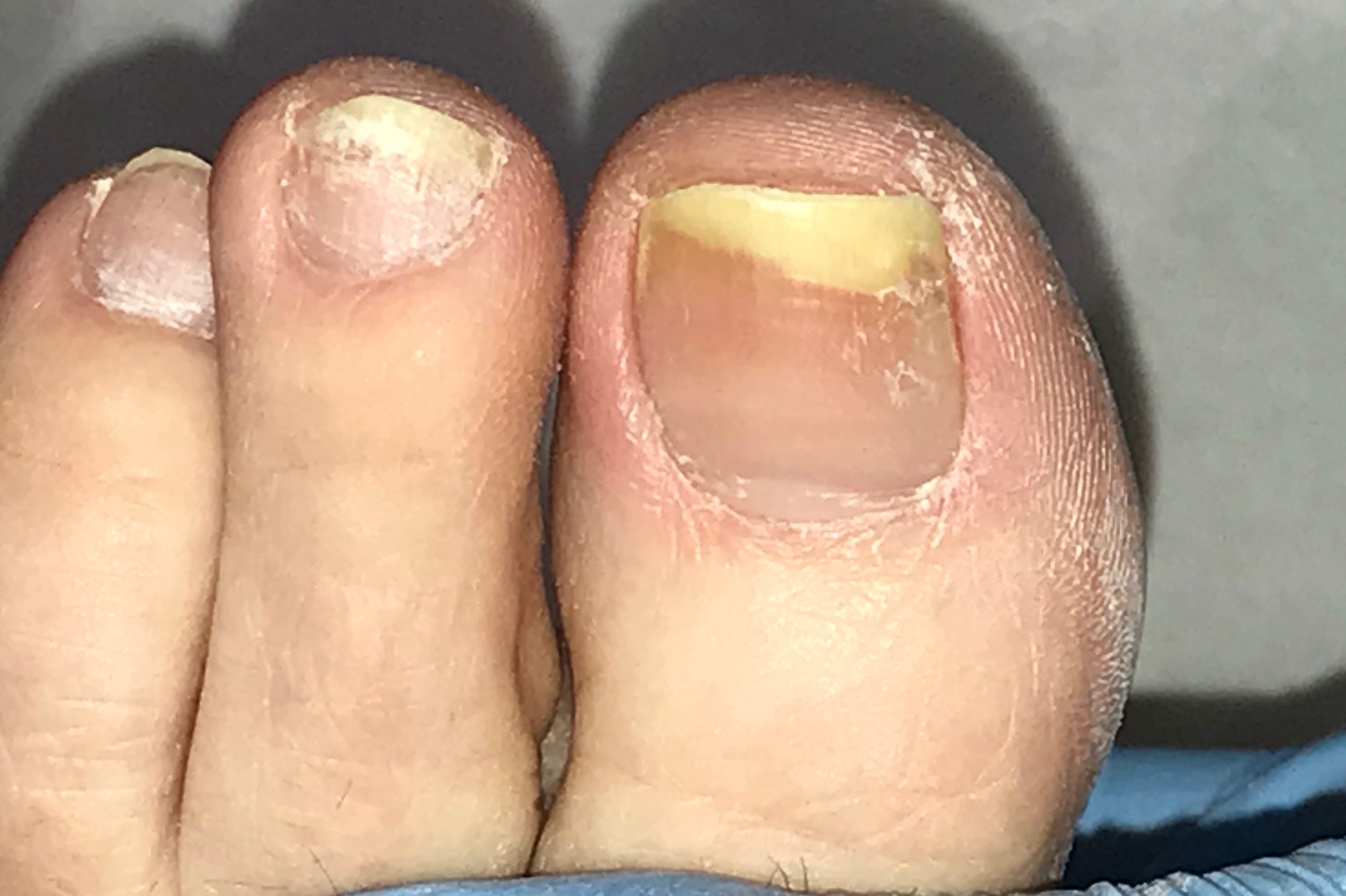
Nail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that affects the nails, typically the toenails. Symptoms of nail fungus can vary but often include:
- Thickened nails: The affected nails may become thicker than usual.
- Brittle or crumbly nails: Nails affected by fungus may become brittle, crumbly, or ragged.
- Distorted shape: The shape of the affected nails may change, becoming distorted or oddly shaped.
- Dull or yellowish color: Nails may become dull, yellow, or discolored.
- Dark color: In some cases, nails affected by fungus may develop dark spots or streaks.
- Separation from the nail bed: The affected nails may lift or separate from the nail bed.
- Pain or discomfort: Nail fungus can sometimes cause pain or discomfort, especially if it becomes severe or if the nails become ingrown.
It’s important to note that nail fungus can be difficult to treat and may require long-term management. If you suspect you have nail fungus, it’s best to see a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
What are the causes of nail fungus?
Nail fungus, or onychomycosis, is usually caused by dermatophytes, a type of fungus that thrives in warm, moist environments. The fungus can enter the skin through small cuts or separations between the nail and the nail bed. Common causes and risk factors for nail fungus include:
- Warm and humid environments: Fungus thrives in warm, moist areas, making certain environments such as swimming pools, locker rooms, and showers more conducive to infection.
- Poor nail hygiene: Not keeping nails clean and trimmed can create an environment where fungus can thrive.
- Trauma to the nail: Injuries to the nail, such as stubbing your toe or having a nail forcefully removed, can make it easier for fungus to enter and infect the nail.
- Wearing tight shoes: Shoes that are too tight can increase the risk of nail fungus by creating a warm, moist environment that is ideal for fungal growth.
- Reduced blood flow to the toes: Conditions that reduce blood flow to the toes, such as diabetes or peripheral artery disease, can increase the risk of nail fungus.
- Weakened immune system: A weakened immune system can make it harder for the body to fight off fungal infections, increasing the risk of nail fungus.
- Age: As people age, their nails can become more brittle and prone to cracking, which can increase the risk of nail fungus.
It’s important to practice good nail hygiene and take steps to prevent nail fungus, especially if you are at higher risk due to factors such as diabetes or reduced blood flow to the toes.
What is the treatment for nail fungus?
Treatment for nail fungus, or onychomycosis, can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the type of fungus involved. Common treatment options include:
- Topical antifungal medications: Over-the-counter or prescription-strength antifungal creams, ointments, or nail lacquers can be applied directly to the affected nails. These medications are often used for mild to moderate cases of nail fungus.
- Oral antifungal medications: Prescription oral antifungal medications, such as terbinafine (Lamisil) or itraconazole (Sporanox), may be prescribed for more severe cases of nail fungus or if topical treatments are not effective. These medications are typically taken for several weeks or months and may have side effects.
- Surgical treatment: In some cases, surgical treatment may be necessary to remove the affected nail. This can help to reduce the fungal load and allow topical or oral antifungal medications to be more effective.
- Laser therapy: Laser treatment is a relatively new approach to treating nail fungus. It involves using a laser to heat and destroy the fungus without causing damage to the surrounding skin and nail.
- Home remedies: Some people may try home remedies, such as vinegar soaks or tea tree oil, to treat nail fungus. While these remedies are generally safe, they may not be as effective as prescription treatments.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan for nail fungus. Untreated nail fungus can lead to complications and may spread to other nails or parts of the body.