Prostate Englargement/BPH: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of prostate enlargement?
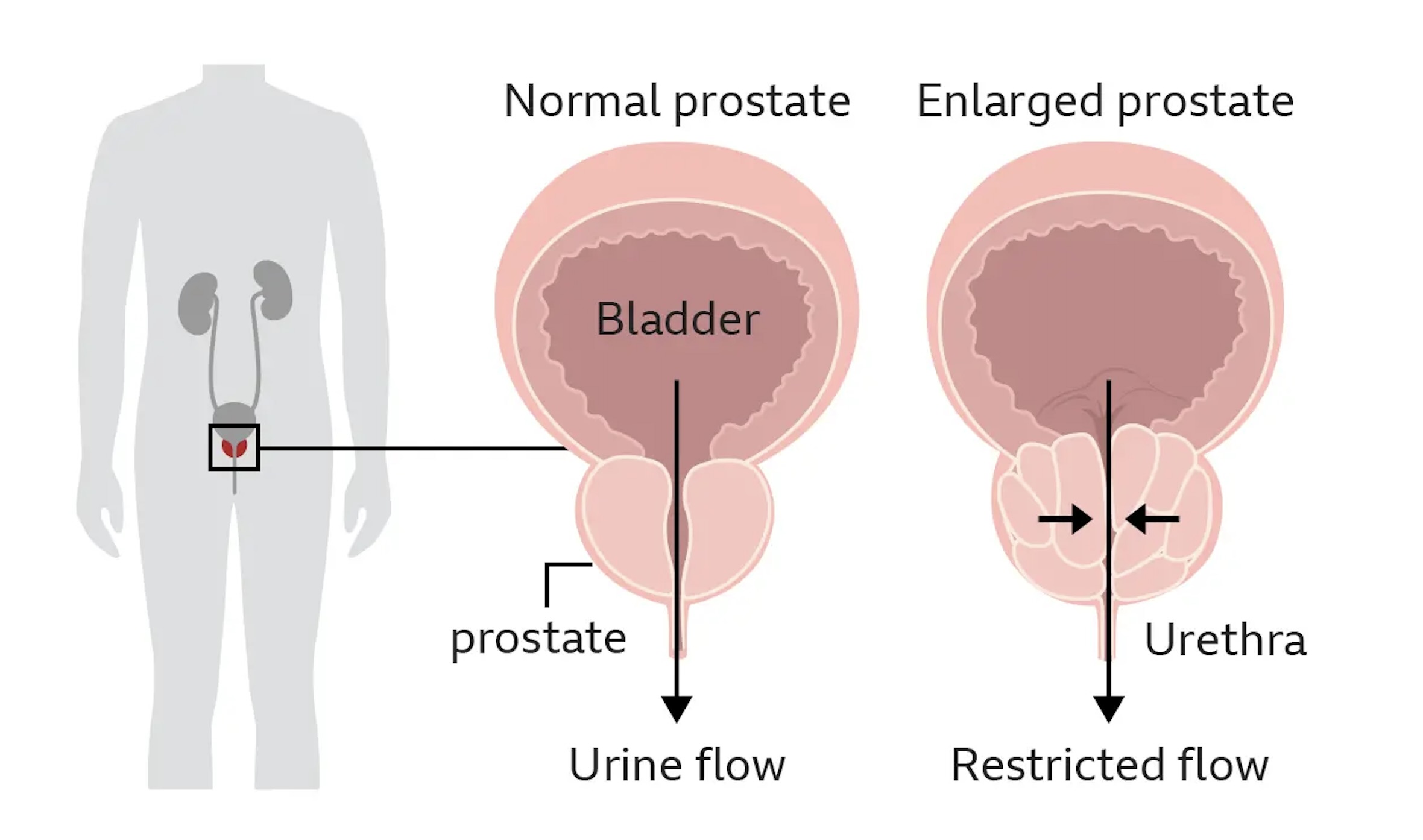
Prostate enlargement, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), can cause various urinary symptoms due to the pressure it puts on the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. The symptoms of prostate enlargement may include:
- Increased frequency of urination: Individuals with prostate enlargement may experience a frequent need to urinate, including waking up multiple times during the night to urinate (nocturia).
- Difficulty starting urination: Prostate enlargement can obstruct the flow of urine from the bladder, leading to difficulty initiating urination. This may cause hesitancy or straining when trying to urinate.
- Weak or interrupted urine stream: The pressure on the urethra caused by an enlarged prostate can result in a weakened or interrupted urine stream, making it more challenging to empty the bladder completely.
- Dribbling at the end of urination: After urination, some men with prostate enlargement may experience dribbling or leakage of urine, even after they feel they have finished.
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder: The obstruction caused by an enlarged prostate may prevent the bladder from fully emptying, leading to a sensation of incomplete urination or the need to return to the bathroom shortly after urinating.
- Urgency: Prostate enlargement can cause a sudden and intense urge to urinate, even if the bladder is not full. This can result in feelings of urgency and the need to rush to the bathroom.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other urinary conditions, such as urinary tract infections, overactive bladder, or prostate cancer. If you experience any persistent or concerning urinary symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare specialist for proper evaluation and diagnosis. Only a healthcare provider can determine the underlying cause of the symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options.
What are the causes of prostate enlargement?
Prostate enlargement, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition that affects many men as they age. The exact cause of prostate enlargement is not fully understood, but it is believed to be influenced by various factors, including:
- Aging: Age is a primary risk factor for prostate enlargement. As men get older, the prostate gland tends to increase in size, a process known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). This enlargement can gradually lead to urinary symptoms due to the pressure it puts on the urethra.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes, particularly in the balance of male hormones such as testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), are thought to play a role in the development of prostate enlargement. DHT, a byproduct of testosterone, is known to promote the growth of prostate cells.
- Genetics: Family history and genetics may also contribute to the risk of developing prostate enlargement. Men with a family history of BPH are more likely to develop the condition themselves.
- Lifestyle factors: Certain lifestyle factors, such as obesity, lack of physical activity, and poor diet, may be associated with an increased risk of prostate enlargement. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through regular physical activity and a balanced diet may help reduce the risk of BPH.
- Other medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome, have been linked to a higher risk of prostate enlargement.
- Medications: Some medications, including certain alpha-blockers, antihistamines, and decongestants, may contribute to prostate enlargement or exacerbate urinary symptoms in men with BPH.
While prostate enlargement is a common condition in aging men, not all men will develop significant symptoms or complications. It is important for individuals experiencing urinary symptoms to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation, diagnosis, and management of prostate health. Treatment options are available to help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life for individuals with prostate enlargement.
What is the treatment for BPH?
The treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate enlargement aims to alleviate symptoms, improve urinary function, and reduce complications associated with the condition. The choice of treatment will depend on the severity of symptoms, the individual’s overall health, and personal preferences. Some common treatment options for BPH include:
- Watchful waiting or active surveillance: For men with mild or asymptomatic BPH, a healthcare provider may recommend regular monitoring of symptoms, lifestyle modifications, and periodic follow-up appointments without immediate treatment.
- Medications:
- Alpha-blockers: Medications such as tamsulosin, alfuzosin, or doxazosin can help relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder, improving urinary flow and reducing symptoms.
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors: Drugs like finasteride or dutasteride can help shrink the prostate gland by blocking the production of hormones that promote its growth.
- Combination therapy: Some men may benefit from a combination of alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors for better symptom relief.
- Minimally invasive procedures:
- Transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT): This procedure uses microwaves to heat and destroy excess prostate tissue.
- Transurethral needle ablation (TUNA): TUNA uses radiofrequency energy to reduce prostate tissue and improve urinary flow.
- Water vapor thermal therapy (Rezūm): This procedure delivers water vapor into the prostate to shrink excess tissue and improve symptoms.
- Surgical procedures:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): TURP is a common surgical procedure that involves removing excess prostate tissue using a special tool inserted through the urethra.
- Laser prostate surgery: Techniques such as laser vaporization, enucleation, or ablation can remove excess prostate tissue using laser energy.
- UroLift: A minimally invasive procedure that uses small implants to lift and hold the prostate tissue away from the urethra, reducing obstruction and improving urinary flow.
- Prostate artery embolization: A minimally invasive procedure that blocks blood flow to the prostate, leading to shrinkage of the gland and symptom improvement.
It is essential for individuals with BPH to discuss treatment options with their healthcare provider, who can recommend the most appropriate approach based on their specific situation. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are important to ensure symptom management and overall prostate health.