Shaken Baby Syndrome: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of shaken baby syndrome?
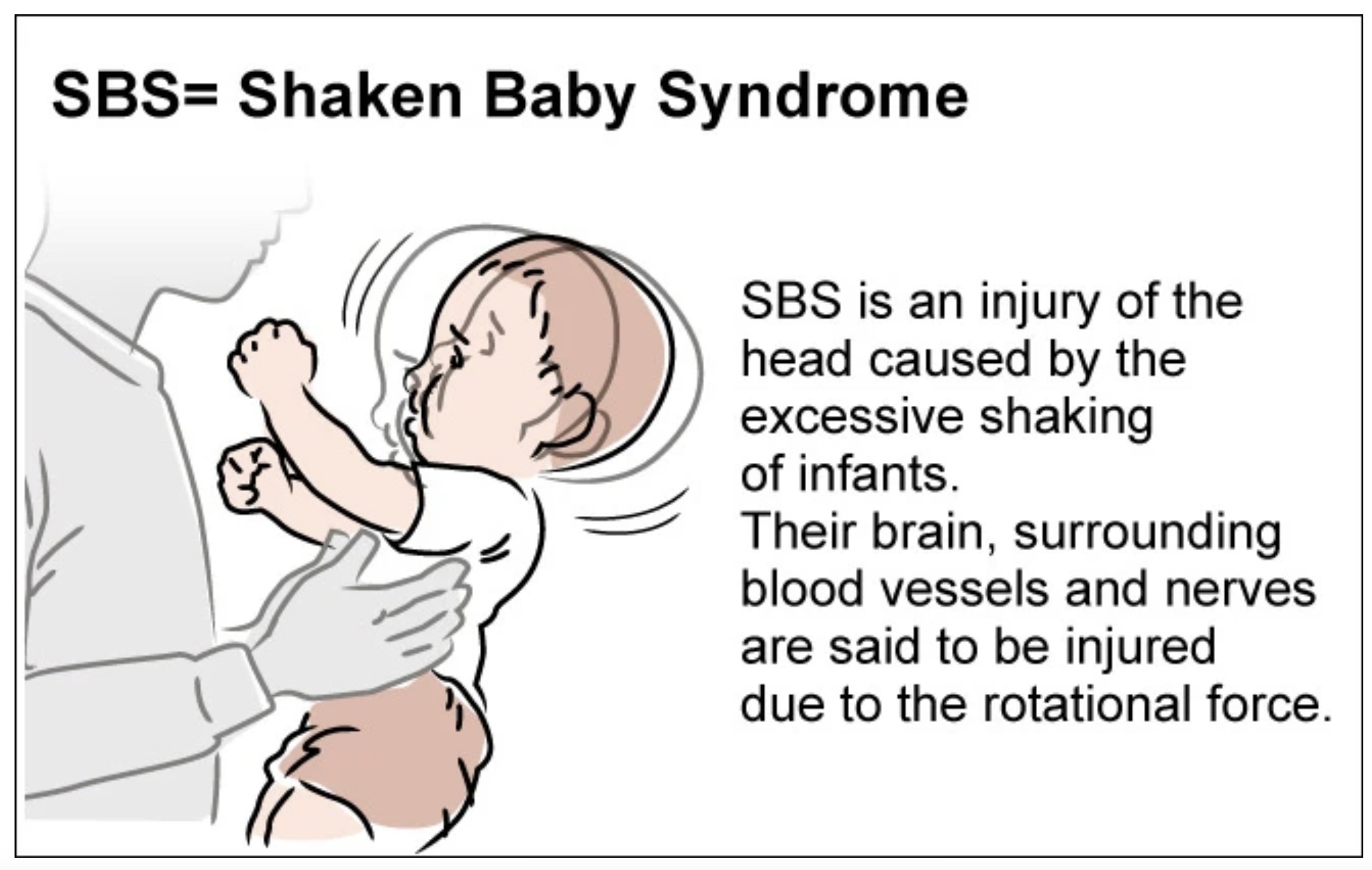
Shaken baby syndrome (SBS) is a serious form of child abuse that occurs when a baby or young child is violently shaken, leading to severe brain injury or death. The symptoms of shaken baby syndrome can vary depending on the severity of the shaking and the age and health of the child, but they often include:
- Brain Injury: Shaking can cause the brain to move back and forth inside the skull, leading to bleeding, swelling, and damage to brain tissue. Symptoms of brain injury can include:
- Irritability or fussiness
- Difficulty staying awake or excessive sleepiness
- Poor feeding or vomiting
- Seizures
- Coma
- Physical Injuries: In addition to brain injury, shaking can cause other physical injuries, such as:
- Neck or spinal cord damage
- Retinal hemorrhage (bleeding in the back of the eye)
- Fractures, particularly of the ribs or bones in the arms or legs
- Behavioral Changes: Children who have been shaken may exhibit changes in behavior, such as:
- Extreme irritability or agitation
- Lethargy or decreased responsiveness
- Changes in eating or sleeping patterns
- Loss of developmental milestones or skills
- Breathing Problems: Shaking can cause breathing problems, including:
- Difficulty breathing
- Irregular breathing
- Apnea (pauses in breathing)
- Other Symptoms: Other symptoms of shaken baby syndrome can include:
- Pale or bluish skin
- Decreased muscle tone or strength
- Excessive drooling
- Inability to lift the head
It’s important to note that these symptoms can be caused by other medical conditions or injuries, so a thorough medical evaluation is necessary to determine if shaken baby syndrome is the cause. Shaken baby syndrome is a preventable form of child abuse, and raising awareness about the dangers of shaking infants and young children is crucial in preventing this devastating condition.
What are the causes of shaken baby syndrome?
Shaken baby syndrome (SBS) is caused by the violent shaking of an infant or young child, typically by a caregiver who becomes frustrated or angry with the child’s crying. The main cause of SBS is shaking, which can result in severe and often irreversible brain damage.
When an infant or young child is shaken, their head moves back and forth rapidly, causing the brain to bounce and twist within the skull. This can lead to bruising, swelling, and bleeding in the brain, as well as damage to the brain tissue. The delicate blood vessels in the brain can also be torn, leading to bleeding around the brain and in the eyes.
The main factors that contribute to the occurrence of shaken baby syndrome include:
- Frustration or Stress: Caregivers who are overwhelmed, stressed, or frustrated, particularly by a child’s crying, may shake the child in an attempt to stop the crying.
- Lack of Understanding: Some caregivers may not be aware of the dangers of shaking a baby or may not understand how easily a baby’s fragile brain can be injured.
- Inexperience: Inexperienced caregivers, such as teenage parents or individuals who have not received proper education about child development and care, may be more likely to shake a baby out of frustration or lack of knowledge about alternative soothing techniques.
- Unrealistic Expectations: Caregivers who have unrealistic expectations about infant behavior, such as expecting a newborn to sleep through the night or never cry, may become frustrated when these expectations are not met.
- History of Abuse: Caregivers who have a history of violence or abuse may be more likely to shake a baby when they become frustrated or angry.
It’s important for caregivers to understand the dangers of shaking a baby and to seek help if they are feeling overwhelmed or stressed. There are many resources available to help parents and caregivers learn how to cope with stress and manage infant crying without resorting to shaking. Preventing shaken baby syndrome requires education, support, and awareness of the dangers of shaking infants and young children.
What is the treatment for shaken baby syndrome?
Treatment for shaken baby syndrome (SBS) focuses on managing the immediate medical needs of the child and addressing the long-term consequences of the syndrome. Since SBS can cause severe brain injury and other complications, the treatment plan is often multifaceted and may include the following components:
- Emergency Medical Care: If a child is suspected of having SBS, they should receive immediate medical attention. Emergency medical care may include stabilizing the child’s condition, addressing any life-threatening injuries, and ensuring proper oxygenation and circulation.
- Neurosurgery: In cases of severe brain injury or bleeding, neurosurgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the brain, repair damaged blood vessels, or remove blood clots.
- Ongoing Medical Care: Children with SBS often require ongoing medical care to manage complications such as seizures, feeding difficulties, and developmental delays. This care may involve a team of specialists, including neurologists, developmental pediatricians, and physical therapists.
- Rehabilitation Therapy: Children with SBS may benefit from rehabilitation therapy to improve motor skills, communication abilities, and cognitive function. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy may all play a role in the child’s recovery.
- Supportive Care: Children with SBS may require long-term supportive care to help them achieve their maximum potential. This may include educational support, social services, and assistance with daily living activities.
- Counseling and Support Services: Families affected by SBS may benefit from counseling and support services to help them cope with the emotional and practical challenges of caring for a child with SBS. This may include support groups, individual counseling, and assistance with navigating the healthcare system.
- Prevention Education: Educating caregivers about the dangers of shaking a baby and providing them with information on alternative ways to soothe a crying baby can help prevent future cases of SBS.
It’s important for caregivers to seek medical attention immediately if they suspect that a child has been shaken. Early intervention and appropriate treatment can help minimize the long-term effects of SBS and improve the child’s overall prognosis.