Tic Douloureux: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of tic douloureux?
Tic douloureux, also known as trigeminal neuralgia, is a condition characterized by severe, shooting or stabbing pain in the face. The pain is typically triggered by certain actions or stimuli, such as chewing, talking, or touching the face. The symptoms of tic douloureux can vary but may include:
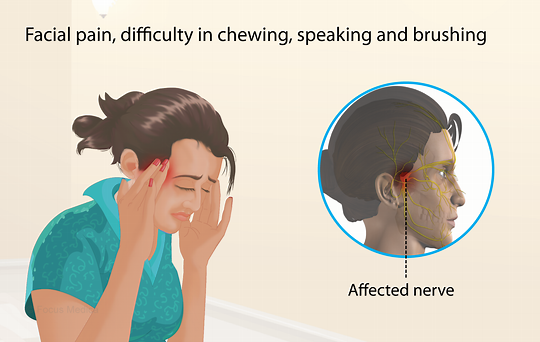
- Severe facial pain: The hallmark symptom of tic douloureux is intense, stabbing, or electric shock-like pain in the face. The pain is typically felt on one side of the face and may be triggered by activities such as eating, talking, or brushing the teeth.
- Episodic pain: The pain of tic douloureux often occurs in episodes or attacks that can last from a few seconds to a few minutes. These episodes can occur multiple times a day or be less frequent, depending on the individual.
- Trigger points: Certain actions or stimuli, known as trigger points, can trigger an episode of pain. Common trigger points include touching the face, chewing, speaking, or even a light breeze on the face.
- Location of pain: The pain of tic douloureux is typically felt in the lower part of the face, including the jaw, cheek, and lower lip. It is often described as sharp, shooting, or like an electric shock.
- Brief duration of pain: The pain of tic douloureux is usually brief, lasting only a few seconds to a few minutes. However, the intensity of the pain can be severe and debilitating.
- Periods of remission: Some people with tic douloureux experience periods of remission, where they are free of symptoms for weeks, months, or even years. However, the condition can recur at any time.
- Symmetrical involvement: In some cases, tic douloureux can affect both sides of the face, although this is less common.
It’s important to note that the symptoms of tic douloureux can vary widely among individuals, and not everyone will experience all of these symptoms. If you experience symptoms of tic douloureux, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What are the causes of tic douloureux?
Tic douloureux, also known as trigeminal neuralgia, is caused by irritation or damage to the trigeminal nerve, which is one of the cranial nerves responsible for sensation in the face. The exact cause of this irritation or damage is often unknown, but several factors may contribute to the development of tic douloureux, including:
- Compression of the trigeminal nerve: Compression of the trigeminal nerve by a blood vessel or tumor can lead to irritation and the development of tic douloureux. This compression is thought to disrupt the normal functioning of the nerve, leading to the characteristic pain of the condition.
- Multiple sclerosis: In some cases, tic douloureux may be associated with multiple sclerosis, a condition that affects the central nervous system. The demyelination (damage to the protective covering of nerve fibers) associated with multiple sclerosis can affect the trigeminal nerve and lead to the development of tic douloureux.
- Other conditions: Certain other conditions, such as a tumor pressing on the trigeminal nerve, a blood vessel pressing on the nerve, or other structural abnormalities in the brain or skull, can lead to irritation of the trigeminal nerve and the development of tic douloureux.
- Aging: Tic douloureux is more common in older adults, and age-related changes in the trigeminal nerve or surrounding structures may contribute to its development.
- Genetics: There may be a genetic component to tic douloureux, as it sometimes runs in families.
- Other factors: Other factors that may contribute to the development of tic douloureux include dental procedures, facial trauma, and infections that affect the trigeminal nerve.
It’s important to note that the exact cause of tic douloureux can vary among individuals, and in many cases, the cause is unknown. If you experience symptoms of tic douloureux, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What is the treatment for tic douloureux?
Treatment for tic douloureux, also known as trigeminal neuralgia, aims to relieve pain and reduce the frequency of episodes. The most appropriate treatment will depend on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s response to treatment. Some common treatments for tic douloureux include:
- Medications:
- Anticonvulsant medications, such as carbamazepine or oxcarbazepine, are often used as first-line treatments for tic douloureux. These medications help reduce the electrical activity in the trigeminal nerve, which can help alleviate pain.
- Other medications, such as gabapentin, pregabalin, or baclofen, may also be used to help relieve pain and reduce muscle spasms in the face.
- Surgery:
- Microvascular decompression surgery is a procedure that involves moving blood vessels away from the trigeminal nerve to relieve compression and reduce pain.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery, such as gamma knife surgery, uses focused radiation to target and damage the trigeminal nerve, which can help reduce pain.
- Other surgical procedures, such as nerve rhizotomy or nerve ablation, may be considered in cases where other treatments have not been effective.
- Nerve blocks:
- Injection of a local anesthetic, such as lidocaine, into the area around the trigeminal nerve can provide temporary relief from pain.
- Physical therapy:
- Physical therapy techniques, such as massage, heat therapy, and gentle stretching exercises, may help reduce muscle tension and improve range of motion in the face.
- Lifestyle modifications:
- Avoiding trigger factors, such as cold air, chewing, or touching the face, may help reduce the frequency of episodes.
- Maintaining good oral hygiene and avoiding dental procedures that may trigger symptoms can also be beneficial.
- Alternative therapies:
- Some people find relief from tic douloureux symptoms with alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, biofeedback, or relaxation techniques. However, the effectiveness of these therapies for tic douloureux is not well-established, and it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any alternative treatments.
It’s important for individuals with tic douloureux to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to their specific needs and symptoms. Prompt and appropriate treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for individuals with tic douloureux.