Tonsillitis: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of tonsillitis?
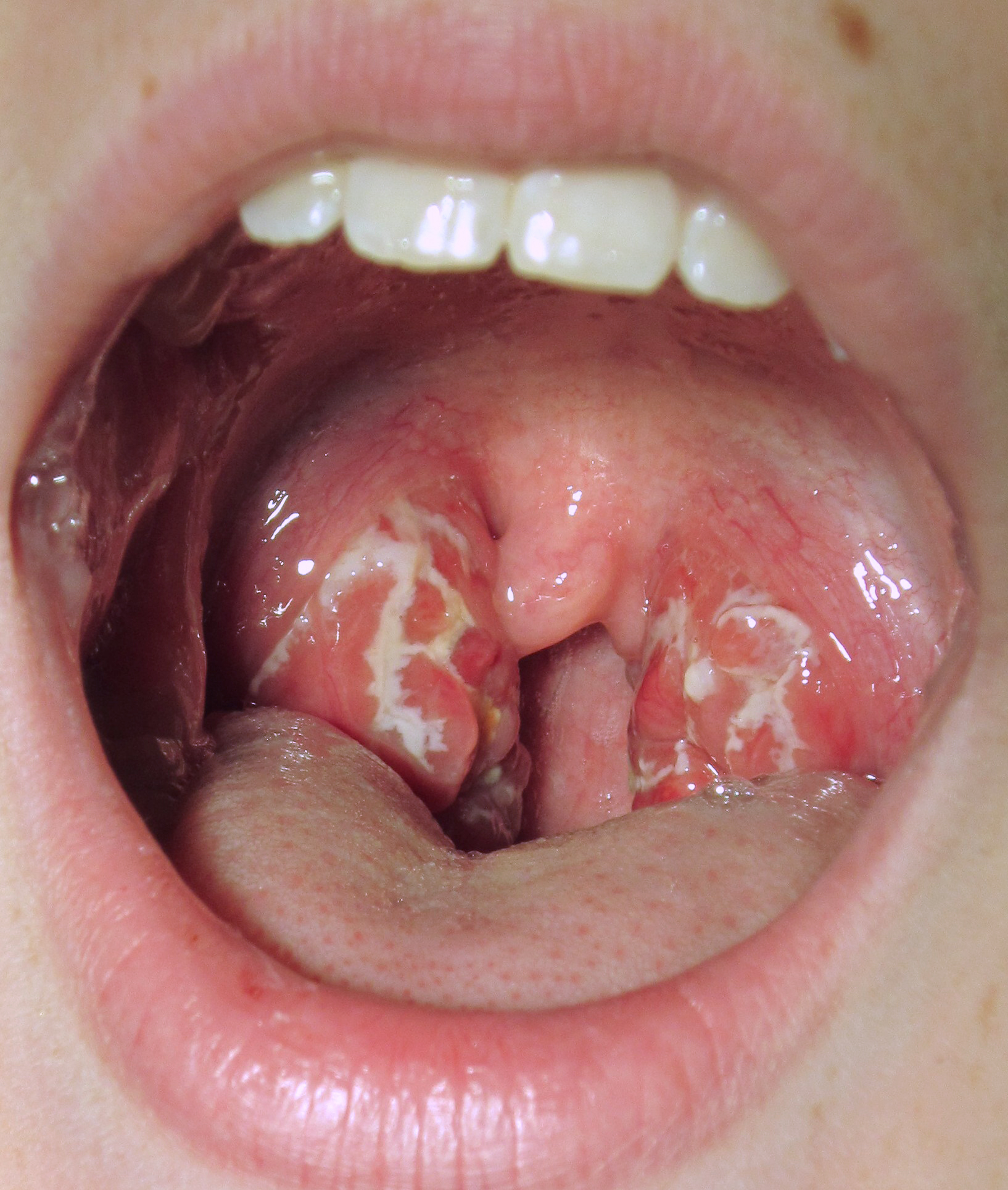
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils, which are two oval-shaped pads of tissue located at the back of the throat. The symptoms of tonsillitis can vary depending on the cause and severity of the inflammation, but common symptoms may include:
- Sore throat: Tonsillitis often causes a sore throat that may be severe and can make swallowing painful.
- Swollen tonsils: The tonsils may appear red, swollen, and may have white or yellow spots or coatings.
- Difficulty swallowing: Swollen tonsils can make swallowing difficult and painful.
- Painful or swollen glands: The lymph nodes (glands) in the neck may become swollen and tender.
- Fever: Tonsillitis can cause a fever, which may be low-grade or high, depending on the severity of the infection.
- Bad breath: Tonsillitis can cause bad breath (halitosis) due to the presence of bacteria and debris in the tonsils.
- Voice changes: Some people with tonsillitis may experience hoarseness or changes in their voice due to throat irritation.
- Headache: Tonsillitis can cause headache, especially if the infection is accompanied by fever.
- Ear pain: The pain from a sore throat caused by tonsillitis can sometimes radiate to the ears, leading to ear pain.
- Difficulty breathing: Severe tonsillitis, especially in children, can cause obstruction of the airway, leading to difficulty breathing.
It’s important to note that not all cases of sore throat are due to tonsillitis, and not all cases of tonsillitis require treatment with antibiotics. If you or your child experience symptoms of tonsillitis, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What are the causes of tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis is most commonly caused by viral or bacterial infections. The main causes of tonsillitis include:
- Viral infections: The majority of cases of tonsillitis are caused by viruses, such as the common cold virus (rhinovirus), influenza virus, adenovirus, or Epstein-Barr virus (which causes infectious mononucleosis or “mono”).
- Bacterial infections: Bacterial infections, particularly by Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococcus), are another common cause of tonsillitis. This type of bacterial infection is known as strep throat and requires treatment with antibiotics.
- Other bacteria: Other bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus or Haemophilus influenzae, can also cause tonsillitis, although less commonly than streptococcal bacteria.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors, such as exposure to tobacco smoke or other irritants, can increase the risk of developing tonsillitis.
- Allergies: Allergies to pollen, dust, mold, or other allergens can sometimes lead to inflammation of the tonsils and tonsillitis.
- Chronic tonsillitis: In some cases, repeated episodes of tonsillitis can lead to chronic inflammation of the tonsils, known as chronic tonsillitis.
- Tonsil stones: Tonsil stones, or tonsilloliths, are small, hard formations of debris and bacteria that can form in the tonsils and cause irritation and inflammation.
- Immune system factors: Factors that weaken the immune system, such as HIV/AIDS or chemotherapy, can increase the risk of developing tonsillitis.
It’s important to note that not all sore throats are caused by tonsillitis, and not all cases of tonsillitis require treatment with antibiotics. If you or your child have symptoms of tonsillitis, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What is the treatment for tonsillitis?
The treatment for tonsillitis depends on the cause of the inflammation (viral or bacterial) and the severity of symptoms. In many cases, tonsillitis will resolve on its own without specific treatment. However, if treatment is needed, it may include:
- Home remedies: Rest, staying hydrated, and using over-the-counter pain relievers (such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen) can help alleviate symptoms. Gargling with warm salt water or using throat lozenges may also provide relief.
- Antibiotics: If tonsillitis is caused by a bacterial infection, such as streptococcus (strep throat), antibiotics may be prescribed. It’s important to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished.
- Antiviral medications: If tonsillitis is caused by a viral infection, antiviral medications may be prescribed in some cases.
- Steroids: In severe cases of tonsillitis, especially if there is significant swelling, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling.
- Surgery: In cases of recurrent tonsillitis or chronic tonsillitis that does not respond to other treatments, a tonsillectomy (surgical removal of the tonsils) may be recommended.
- Pain management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate pain and reduce fever. Throat lozenges or sprays may also provide temporary relief.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment, especially if symptoms are severe or persistent. Untreated bacterial tonsillitis can lead to complications such as abscess formation or rheumatic fever, so it’s important to seek medical attention if you suspect you or your child have tonsillitis.