Chalazion: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What are the symptoms of a chalazion?
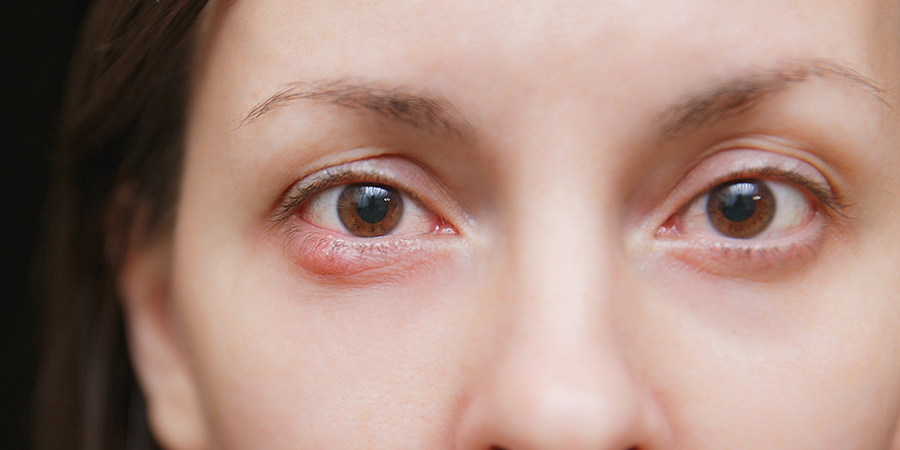
A chalazion is a small, usually painless lump or swelling that appears on the eyelid. It is caused by a blocked oil gland. Common symptoms of a chalazion include:
- A small lump or swelling on the eyelid.
- Tenderness or sensitivity in the affected area.
- Redness and swelling around the eyelid.
- Blurred or decreased vision if the chalazion is large enough to press on the eye.
Chalazia are often confused with styes, which are infections of the eyelid glands, but chalazia are not usually painful and tend to be larger. If you suspect you have a chalazion, it’s best to consult with an eye care professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What is the treatment for a chalazion?
Treatment for a chalazion typically involves self-care measures and medical interventions. Here are some common approaches:
- Warm compresses: Applying a warm compress to the affected eyelid can help soften the hardened oil that is blocking the gland, promoting drainage and healing. This can be done for 10 to 15 minutes, several times a day.
- Eyelid hygiene: Keeping the eyelids clean can help prevent further blockages and infections. Using a mild cleanser or baby shampoo diluted in warm water, gently scrub the base of the eyelashes to remove debris and bacteria.
- Medicated eye drops or ointments: Your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotic eye drops or ointments if there is a risk of infection or if the chalazion is associated with blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids).
- Steroid injections: In some cases, a healthcare provider may inject a corticosteroid medication into the chalazion to reduce inflammation and promote faster healing.
- Surgical drainage: If the chalazion does not respond to other treatments or is large and causing vision problems, a minor surgical procedure called incision and curettage may be performed. This involves making a small incision in the eyelid to drain the contents of the chalazion.
It’s important to consult with an eye care professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan for a chalazion. They can recommend the best course of action based on the size, location, and severity of the chalazion.
What are chalazia?
A chalazion (plural: chalazia) is a common eyelid condition that involves the formation of a small lump or swelling on the eyelid. Chalazia are typically painless and usually develop on the upper eyelid, although they can also occur on the lower eyelid. They are caused by a blockage of the meibomian glands, which are oil-producing glands located in the eyelids.
The blockage leads to the buildup of oil in the gland, causing the gland to become swollen and inflamed. Over time, the swollen gland may form a firm, round lump on the eyelid, which is known as a chalazion. Chalazia are usually not serious and often resolve on their own without treatment. However, they can sometimes become larger or more persistent, requiring medical attention.
Treatment for chalazia may include:
- Warm compresses: Applying a warm compress to the affected eyelid several times a day can help soften the oil in the blocked gland and promote drainage.
- Eyelid hygiene: Keeping the eyelids clean and free of debris can help prevent further blockage of the meibomian glands.
- Topical antibiotics: In some cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotic ointment to help prevent infection in the affected area.
- Steroid injections: For larger or more persistent chalazia, a healthcare provider may inject a corticosteroid medication into the lump to help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Surgical drainage: In rare cases, a chalazion may need to be surgically drained if it does not respond to other treatments. This procedure is typically performed by an ophthalmologist and involves making a small incision in the eyelid to drain the contents of the chalazion.
It’s important to consult a healthcare provider if you have a chalazion or any other eyelid lump or swelling, especially if it is causing symptoms such as pain, redness, or vision changes. A healthcare provider can determine the appropriate treatment and rule out any underlying conditions that may be causing the eyelid lump.