What is Biofeedback Therapy?
Biofeedback therapy is a mind-body technique that involves measuring a person’s bodily functions, such as brain waves, heart rate, breathing patterns, muscle tension, and skin temperature, and providing this information in real-time to help the person gain greater awareness and control over these functions.
The main goal of biofeedback therapy is to teach individuals how to consciously regulate their body’s involuntary processes, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and muscle tension, through techniques like deep breathing, visualization, and relaxation exercises. By becoming more aware of these physiological processes, individuals can learn to modify their responses to stress, pain, and other conditions.
During a biofeedback session, sensors are attached to the person’s body to measure the specific bodily function being targeted. This information is then displayed on a monitor or through auditory signals, allowing the individual to see or hear their physiological responses in real-time. With the guidance of a biofeedback therapist, the person learns relaxation and visualization techniques to alter these physiological responses.
Biofeedback therapy can be used to manage a variety of conditions, including:
- Headaches and migraines
- Chronic pain conditions
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Anxiety and stress-related disorders
- Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Urinary incontinence in men and in women
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Insomnia and sleep disorders
- Neuromuscular disorders
- Raynaud’s disease
The therapy aims to teach individuals self-regulation skills that can help them better manage their symptoms and improve overall well-being. It is often used in conjunction with other treatments, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, medication, or physical therapy, as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Biofeedback therapy is generally considered safe and non-invasive, although some individuals may experience mild side effects, such as fatigue or muscle soreness, especially when first learning the techniques.
What does biofeedback therapy measure?
Biofeedback therapy can measure and provide feedback on various physiological functions and processes in the body. The specific bodily functions measured during biofeedback depend on the condition being treated and the therapeutic goals. Here are some common physiological measures used in biofeedback therapy:
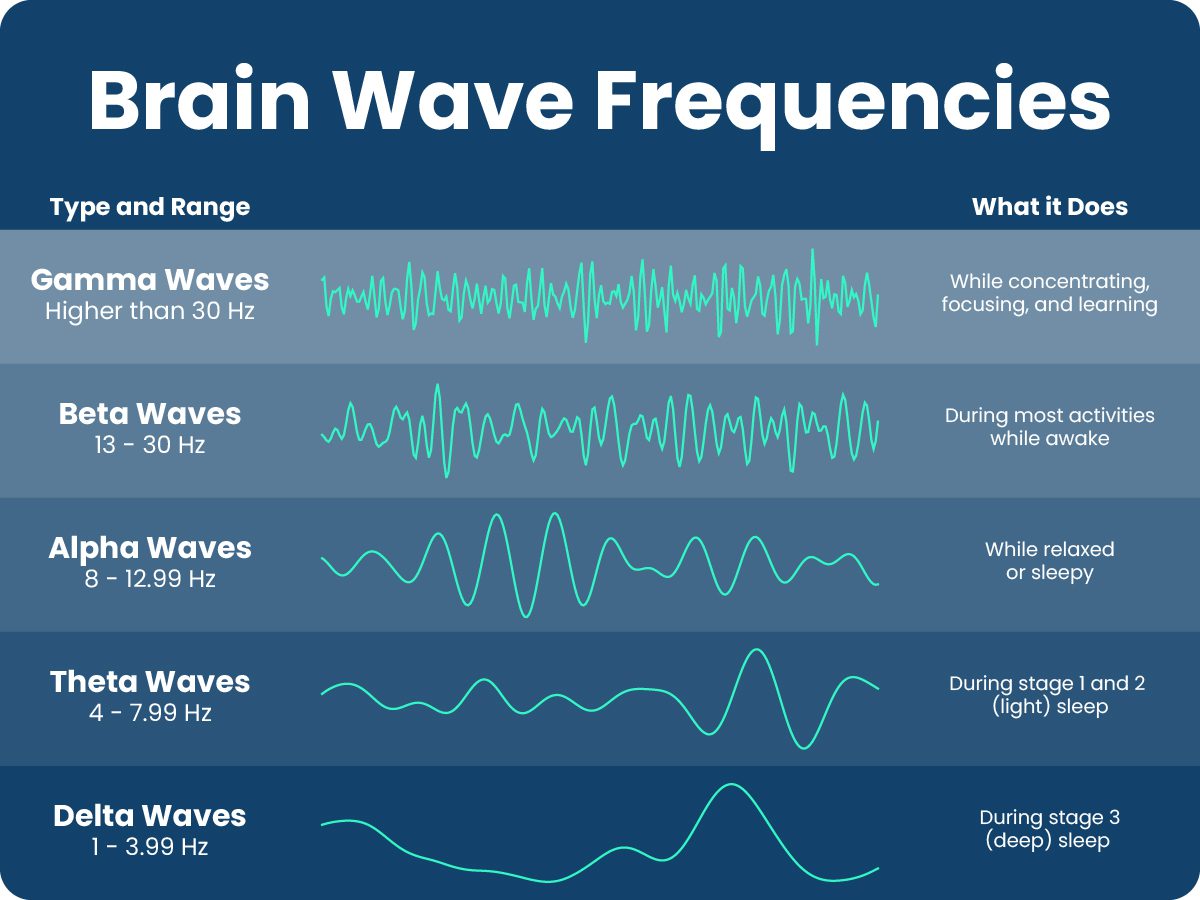
- Brain waves (electroencephalography or EEG):
- Measures electrical activity in the brain
- Used for conditions like ADHD, anxiety, insomnia, and headaches
- Heart rate (electrocardiography or ECG/EKG):
- Measures the electrical activity of the heart
- Used for conditions like hypertension, anxiety, and stress management
- Muscle activity (electromyography or EMG):
- Measures the electrical activity of muscles
- Used for conditions like chronic pain, headaches, and neuromuscular disorders
- Skin temperature (thermal biofeedback):
- Measures changes in skin temperature, which can reflect stress levels
- Used for conditions like Raynaud’s disease, migraine headaches, and anxiety
- Respiration (respiratory biofeedback):
- Measures breathing patterns, such as rate and depth
- Used for conditions like asthma, anxiety, and stress management
- Sweat gland activity (electrodermal activity or EDA):
- Measures changes in sweat gland activity, which can reflect emotional arousal
- Used for conditions like anxiety, phobias, and stress management
- Blood pressure (blood volume pulse or BVP):
- Measures changes in blood pressure and blood flow
- Used for conditions like hypertension, chronic pain, and stress management
The biofeedback equipment used to measure these physiological functions typically includes sensors attached to the body, which are connected to a monitoring device that displays the data in real-time. By observing and interpreting these measurements, individuals can learn to consciously regulate and control these bodily functions through various techniques, such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or visualization exercises.